 |
 |
| Korean J Anesthesiol > Volume 71(6); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
In infants and small children, ultrasound (US) guidance provides ample anatomical information to perform neuraxial blocks. We can measure the distance from the skin to the epidural space in the US image and can refer to it during needle insertion. We may also visualize the needle or a catheter during real-time US-guided epidural catheterization. In cases where direct needle or catheter visualization is difficult, US allows predicting successful puncture and catheterization using surrogate markers, such as dura mater displacement, epidural space widening due to drug injection, or mass movement of the drug within the caudal space. Although many experienced anesthesiologists still prefer to use conventional techniques, prospective randomized controlled trials using US guidance are providing increasing evidence of its advantages. The use of US-guided regional block will gradually become widespread in infants and children.
Similar to postoperative pain management in adults, the goals of postoperative analgesia in children are pain eradication, expedient recovery to daily activities, and prevention of progression of acute postsurgical pain to chronic pain or hyperalgesia. Acute postoperative pain is reported to progress to chronic pain in 10%–50% of adults [1] and 20% of children who undergo major surgery [2]. Therefore, acute postoperative pain should be treated aggressively. Traditionally, opioids have been used for postoperative pain relief in children; however, they are no longer recommended as the first-line analgesics owing to their side effects [3]. Currently, multimodal analgesia is increasingly preferred, where non-opioid analgesics are combined with a small dose of opioids or regional blocks [3,4].
Epidural blocks are commonly used for pediatric anesthesia and analgesia after abdominal, pelvic, or thoracic surgery. Epidural block in children, due to the smaller body size, requires considerable experience and a high level of skill. The distance to the epidural space is short in infants and children, and changes in body habitus with increasing age are variable, making it difficult to predict the distance from the skin to the epidural space [5]. Furthermore, the connective tissue is soft, thereby limiting the tactile feedback of loss of resistance (LOR) in identifying the epidural space [5]. Besides, since regional block in children is usually performed under deep sedation or general anesthesia, subjective warning signs of neural injury during needle insertion cannot be detected. The application of US is particularly useful for regional epidural block in infants and small children, since incomplete vertebral ossification facilitates the penetration of the US beam into the posterior vertebral column and makes identification of spinal structures easier. Even though the evidence of benefit for US-guided neuraxial blocks is insufficient relative to US-guided peripheral nerve blocks, US has clearly improved the success rate of first puncture and shorten the block performance time in neuraxial blocks [5,6].
In this review, I describe the past and present applications of epidural and caudal block, which are representative types of central neuraxial block, ultrasonographical anatomy and procedures performed under US guidance. I hope that this review will be useful in understanding the special features of epidural and caudal block in children.
Although epidural and caudal block are now frequently used in intraoperative and postoperative analgesia for pediatric surgery, they were initially limited to anesthesia for urological procedures in children. In 1933, Meredith Campbell [7], a urologist, first reported the use of caudal anesthesia for cystoscopies in children; Roderie Sievers first reported on lumbar epidural anesthesia for cystoscopy in 1936; it was revived later by Schneider who reported over 6,500 infants who underwent urological procedures under lumbar epidural anesthesia in 1951 [8]. Based on a report by the Italian surgeon Achille Mario Dogliotti in 1933 [9], Francis G Ruston, while serving in the Canadian Army Medical Corps, administered epidural anesthesia to soldiers at a military hospital overseas for the first time towards the end of World War II [10]. In the early 1950s, Ruston [10] performed single-shot epidural or caudal anesthesia under codeine sedation in 77 neonates and infants undergoing abdominal or pelvic surgery for conditions such as pyloric stenosis. Ruston used a thoraco-lumbar epidural approach, inserting a 22 G short-beveled blunt needle in the intervertebral spaces between T10–L1 or L2–L4, depending on the type of surgery. For identifying the epidural space, Ruston [11] applied a hanging drop technique using a saline-filled syringe attached to the needle. In his next report, Ruston [12] described four different methods for identifying the epidural space, including: the LOR method, the fluid disappearing (hanging drop) method, detection of negative pressure using a manometer, and withdrawal of the needle after dural puncture. Of these, until now, the LOR method has been the most commonly used method. Ruston also described an anesthetic technique combining continuous epidural and general anesthesia, but this method was largely ignored at that time.
Epidural and caudal blocks were used only sporadically until the late 1980s, when Ecoffey et al. [13] and Murat et al. [14] revived the technique of combining continuous lumbar and thoracic epidural anesthesia with general anesthesia during surgery in infants and children. In 1988, Bosenberg et al. [15] introduced continuous thoracic epidural anesthesia via the caudal route; this method still remains in use.
In infants and children, central neuraxial block is an important modality for acute postoperative analgesia in addition to combined anesthesia. The introduction of US has greatly improved the performance of central neuraxial block. US guided neuraxial block in children was first performed by Chawathe et al. [16]. The authors performed ultrasonography of the spinal region within 24 hours after lumbar epidural catheterization in 12 neonates and infants; they were able to visualize the catheter within the epidural space in 10 subjects less than 5 months of age. Subsequently, Rapp et al. [17] used US examination before the procedure to measure the distance from the skin to the ligamentum flavum in 23 infants and children. The authors referred to this measurement during needle insertion to identify the epidural space by LOR and were able to successfully advance the catheter under a paramedian US imaging. In a study of 180 infants and children, Kil et al. [18] also measured the distance from the skin to the ligamentum flavum on US images prior to lumbar epidural puncture. They demonstrated that the measured distance is highly correlated with depth of needle insertion in the epidural space, similar to the results reported by Rapp et al. Willschke et al. [19] performed epidural puncture under real-time US guidance in 35 neonates, and used drug injection to verify location of the needle within the epidural space. However, even though they reported that catheter could be identified within the epidural space using surrogate markers, such as drug injection or tissue movement, these results will likely depend upon the quality of images generated by the US machine. These reports led to increased use of epidural block in neonates, infants and children, and have especially improved the efficacy and overall outcomes of US-guided thoracic epidural block [20].
The universally used caudal block has a high success rate, even though it varies depending on the experience of the practitioner. US is not an essential method for performing a caudal block. In a large-scale study (2015), using the pediatric regional anesthesia network (PRAN) database, Suresh et al. [21] reported that US was used only in 2.4% of 18,650 total cases of caudal block, and the frequency of US usage during this procedure decreased after 2010. However, anatomical variations of the sacral hiatus and sacral cornua, obesity, and excessive subcutaneous fat in the sacral region can make a landmark-based caudal approach difficult. Dalens and Hisnaoui [22] performed caudal block in 650 children and reported a high overall success rate (96%), however, there was a high rate of multiple puncture (25%). Veyckemans et al. [23] reported that identification of the sacral hiatus was difficult in 11.2% of 1,100 pediatric patients 7 years or younger. Among 18,650 cases analyzed by Suresh et al. [21], a block failure rate of 1% was reported; however, the rate of repeated puncture was not investigated. Thus, the overall success rate of caudal block is very high, but repeated punctures may frequently occur. There are several possible causes of repeated punctures, including difficult hiatus identification, narrow caudal space below hiatus, and presence of excessive fat in the sacral region. In two randomized controlled trials comparing US-guided caudal block with a conventional approach reported in 2013 and 2018, the overall success rate of block was similar, however, US-guided block resulted in a significantly higher first puncture success rate, and a significantly lower rate of complications, including intravascular and subcutaneous injection [24,25]. Additionally, Ponde et al. [26] reported accurate advancement of the epidural catheter to the expected lumbar or thoracic level through the caudal hiatus under US guidance in neonates and infants. Therefore, for performing caudal block in children, it would be preferable to use US guidance when considering the risk-benefit and cost-effectiveness ratio.
Recently, several animal studies have demonstrated that commonly used general anesthetics (benzodiazepine, barbiturates, ketamine, propofol, isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane) cause several neurological changes in the developing brain and result in long-lasting behavioral and cognitive changes [27–29]. Conflicting results have been reported in humans, and the evidence is only correlative [30,31]. However, in 2016 the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned that “repeated or lengthy use of general anesthetic and sedation drugs during surgeries or procedures in children younger than 3 years or in pregnant women during their third trimester may affect the development of children’s brains” [32]. In 2017, this statement was updated as “exposure to these medicines for lengthy periods of time or over multiple surgeries or procedures may negatively affect brain development in children younger than 3 years” [33]. Therefore, in small children, especially in neonates and infants, the duration of anesthesia should be kept as short as possible, and it is recommended to use methods that allow acute postoperative pain to be managed with a lower dose of anesthetic by combination with regional anesthesia [29].
Although caudal block can rarely result in dura puncture, it is generally safe and easy to perform. In a large-scale analysis by Suresh et al. [21], the authors concluded that caudal block is a safe procedure in children when an appropriate dosage of local anesthetics is used. With epidural block, there is always concern about neurologic injuries. In particular, unlike in adults, in children, epidural block is almost always performed under deep sedation or general anesthesia. If awake, infants and children are likely to move during palpation, needle placement and even on feeling a cold US probe. This may increase the risk of nerve injury during needle placement. In 2015, The Joint Committee of European Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Therapy and the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine suggested that high-level evidence for the safety of central neuraxial block in small children is still not available. However, they also concluded that, based on evidence category B2 (observational studies with associative statistics) and B3 (noncomparative observational studies with descriptive statistics), the performance of pediatric regional block under deep sedation or general anesthesia is acceptable in terms of safety and could be a standard of care [34]. Nevertheless, the possibility of neurologic injury due to epidural block does exist, and it is a grave complication that always requires caution. The use of US guidance for epidural block is expected to improve both block-related and procedure-related outcomes.
The vertebral column and the spinal cord of infants and children show significant differences compared to adolescents and adults. At birth, the conus medullaris and the dural sac end (DSE) are located at the L4 and S3–S4 levels. Due to differences in growth rates between the spinal cord and the spinal canal, they reach the T12–L1 and S2 levels as observed in adults only by the end of the second year. The intercristal (Tuffier’s) line is located at the L3–L4 level in adults, but at the L4–L5 or L5–S1 level in children. The vertebrae are mostly cartilaginous at birth as they are not completely ossified; the laminae at the L1–L4 level fuse progressively during the first year of life, but ossifies after 5 years of age at the L5 level [35]. In children, the fascia and sheaths within the epidural space are loosely attached to the nerve trunk and muscles, and up to 6–8 years of age, the epidural fat is very fluid. This enables easy spread of local anesthetics, especially their distal spread. In addition, incomplete myelination of the nerve fibers enables good quality block even with a low concentration of local anesthetics. On the other hand, because drug leaks into the paravertebral space where spinal nerve roots reside, a relatively large volume of local anesthetics is required to obtain the same block level with epidural anesthesia in adults [36].
In small children, the L4–L5 interspace is most commonly selected for epidural catheterization. However, in a fluoroscopy study in children, Kim et al. [37] discovered that the lower the level of the epidural catheter insertion, the higher the failure rate to reach the target level. From one year of age onwards, the frequency of the catheter reaching the expected level decreases, and doubling back or coiling of the catheter is not uncommon [37,38]. This is thought to be related to the development of the lumbosacral curvature due to body habitus after that age, related to standing and walking, which interferes with catheter advancement [36,38]. Therefore, in order to place the epidural catheter tip at the level that can provide effective analgesia for a given surgery type or incision level, it is preferable to use the approach at a site close to the level of the incision and to advance the epidural catheter by only 2–3 cm [5]. Table 1 show the spinal segments to use as analgesic targets for different surgical sites and epidural drug infusion rates for postoperative analgesia. When combining epidural and general anesthesia, a bolus of 0.5–1.0 ml/kg of 0.25% bupivacaine or 0.3% ropivacaine is recommended to establish the block [39]. Sympathetic blockade is well tolerated in children with very little change in blood pressure and heart rate [14,39].
The posterior vertebral column is cartilaginous in infants and small children, which enables easy penetration of the US beam offering good quality images of the spinal structures. The child is placed in a lateral position with the hips fully flexed position. A high-frequency probe of 7–13 MHz is used to the scan from the sacral to thoracic level, and to confirm the point of the termination of the conus medullaris and the dural sac (Fig. 1). In Fig. 2A, the posteriorly located, deep, circular, intensely hyperechoic dura mater encloses an anechoic (black) space filled with cerebrospinal fluid; the hyperechoic ligamentum flavum is visible dorsally. In Fig. 2B, the conus medullaris, nerve roots, and the cauda equina fibers can be observed. These neuraxial structures are readily visible before 3 months of age, after which the visibility gradually decreases [5,40,41]. At the cervicothoracic and upper lumbar levels, where ossification occurs at an earlier stage, visualization is even more difficult, but the dura matter is easier to differentiate. Hence, it is preferable to acquire an acoustic window in the longitudinal paramedian plane at this level.
After selecting a puncture site according to the type of surgery, the distance from the skin to the ligamentum flavum is measured to serve as a reference during needle insertion. In the transverse view, the depth of the epidural space may be underestimated due to the compression of the soft tissue in the intervertebral space by the probe; hence, measurement in the longitudinal or paramedian view is preferable [42]. Following sterile preparation, the assistant positions the US probe superior to the puncture site in the paramedian plane to enable the dura mater and ligamentum flavum to be visualized, enabling free use of both hands by the operator. In infants and children, similar to adults, the epidural space has a triangular shape (Fig. 2A). Hence, the needle insertion must be through a midline approach, to enter the widest epidural space. The epidural space in infants is very narrow, usually less than 2 mm wide [5,43], whereas the bevel length of commonly used pediatric epidural needles is 1.5–2 mm. Consequently, in infants and small children, the needle should be angulated in a cephalad direction to locate the needle tip within the epidural space [43]. When the needle tip is seen to pass through the ligamentum flavum and enter the epidural space on the US images, its position is confirmed by LOR. Air or saline could be used for LOR, depending on the operator preference. Complications including nerve root compression, pneumocephalus, incomplete analgesia, and venous air embolism have been reported with the air-LOR technique, while the saline-LOR technique could present problems including dilution of the local anesthetic solutions due to excess saline, and difficulty in identifying accidental dural puncture [34]. Nevertheless, the saline-LOR technique is preferred [34]. After the LOR test, when a small volume of saline or local anesthetic is injected, ventral displacement of the dura mater and widening of the epidural space can be observed on US images (Fig. 3A). When the epidural catheter is inserted, it is recommended to push the needle hub about 30–40° toward the skin in a caudad direction, to decrease the angle between the needle tip and the dura mater in a cephalad direction within the epidural space. This maneuver helps with catheter insertion and advancement [43]. In neonates and young infants, the catheter can be visualized by US imaging after placement in the epidural space by observation in multiple planes (Fig. 3B). When detection is difficult, saline or drug injection can be used to verify the displacement of the dura mater, movement of the surrounding tissue, or spread of the local anesthetic solution. At the thoracic level, the epidural space is narrower than that in the lumbar region, and US visualization is impaired; however, the dura mater can be easily detected.
At the thoracic level, up to the age of 9 months, the needle can be inserted almost perpendicular to the skin. As the spinal curvature develops with age, the needle needs to be inserted with a more cephalad orientation, similar to the midline approach in adults [36]. In older children, the angle between the spinous process and vertebral arch is sharper; hence, a longitudinal paramedian plane approach, which uses a low-frequency convex probe, is more useful compared to a high-frequency linear probe.
In children, especially infants, damage to the ossification nuclei can cause impairment of normal bone growth and ossification; hence, care should be taken to prevent boney contact during needle insertion, and the use of sharp needles should be avoided [36].
The technique of caudal block is relatively easy to familiarize. It is generally used for intraoperative or postoperative analgesia in infraumbilical surgery, including some types of surgery involving the lower extremities, in children under 7 years of age. For older children, thickening of the sacrococcygeal ligament makes it difficult to identify the sacral hiatus, and hence, the block is often not performed at the hiatus [36]. The sacral vertebral plate is less ossified at birth, and the sacral vertebrae are connected by cartilage; the plate undergoes progressive ossification and union and becomes a single structure after puberty [35].
In contrast, posterior fusion at the S4 and S5 levels remains incomplete, and this region is covered by the sacrococcygeal ligament, formed by a tight connection between the ligamentum flavum and other sacral ligaments. The sacral hiatus assumes a triangular shape limited bilaterally by the sacral cornua, which are the inferior articular processes of S5, and the lower end of the dorsal sacrum [35]. This is the entrance to the sacral canal, and a needle can be inserted into the sacral epidural canal through the hiatus. The extent of protrusion of the sacral cornua varies between individuals, and they can be asymmetrical or blunt; in adults, the hiatus can even be obliterated by a complete fusion of the lamina [35,36].
The child is placed in a lateral position with the hips, maximally flexed. The lumbosacral area is observed for the presence of any cutaneous stigmata, such as dimples. Recently, US examination of the vertebrae has been commonly used when stigmata are detected in the gluteal area immediately after birth; however, depending on the circumstances of birth, these signs could often be missed. Among children who undergo surgery for urogenital anomalies, those with minor stigmata, and occasionally with no stigmata, often have occult spinal dysraphisms, such as a tethered spinal cord with lipoma [44]. Hence, a detailed observation is required. The US probe is placed transversely over the coccyx and scanning is performed in the cephalad direction. If the bilateral cornua reveal a “frog-eye sign” and the hyperechoic “hump” (sacrococcygeal ligament) appears, the anechoic space between the “hump” and hyperechoic dorsum of the pelvic surface of the sacrum is the sacral hiatus (Fig. 4A).
In the longitudinal plane, the thick linear sacrococcygeal ligament appears hyperechoic covering the space from inferior S3 to the distal end of the sacrum, and an anechoic caudal space can be observed (Fig. 4B). Moving in a cephalad, the dural sac end, cauda equina fibers, filum terminale, and conus medullaris can be seen (Fig. 1). After sterile preparation, the probe is placed close to the apex of the triangular area formed bilaterally by the sacral cornua and the tip of the dorsal sacrum. This ensures a wider distance between the sacrococcygeal ligament and the base of the sacrum, and therefore, helps select a location where the caudal space is the widest (Fig. 5). In this transverse view, the needle tip is placed at the point of insertion, and the probe is shifted to the longitudinal plane. If the angle is adjusted with real-time imaging as the needle is advanced, it can be easily inserted into the caudal space (Fig. 6). Once the needle has been advanced into the caudal space, the local anesthetic solution may be injected and mass movement of the drug observed. The needle placement and success rate of caudal block are highly dependent on operator skill, and real-time US-guidance does not clearly improve the overall success rate compared to conventional methods. However, as described above, US-guided caudal block increases the success rate of insertion at the first attempt and can reduce complications including vascular puncture and subcutaneous bulging [23,24].
During caudal block, short beveled, a relatively blunt needle should be used. Sharp needle can easily injure or even cut across the sacral base, causing damage to the pelvic or retroperitoneal organs [36].
The dose of local anesthetics is determined based on the type of infraumbilical surgery. Most commonly, the Armitage formula (0.2% bupivacaine, 0.20%–0.25% levobupivacaine or ropivacaine; perineal surgery 0.5 ml/kg, inguinal hernioplasty 1 ml/kg, and orchiopexy 1.25 ml/kg) is used for dose calculation [45].
Although experienced practitioners can perform caudal block through the sacral hiatus with relative ease, occasionally, it is difficult identify the hiatus, which can lead to multiple punctures or failure of needle insertion. In these cases, a trans-sacral approach may be used as an alternative method. Dalens and Chrysostome [46] also attempted inserting the epidural catheter at S1–S2 in children, but in 1987, Busoni and Sarti [47] suggested that a trans-sacral approach at the S2–S3 level was a useful alternative technique to the hiatal approach. The S2–S3 interspace can be easily palpated slightly inferior to the line connecting the posterior superior iliac spines on both sides. At this site, similar to lumbar epidural puncture, the needle is inserted perpendicularly (Fig. 7). The sacral hiatus is the distal part of the caudal space, and the depth of the space at this site was found to be 3–3.5 mm in US studies [48,49], while it was twice as deep at the S2–S3 level [49]. In Fig. 5, the depth of the caudal space can be compared at each level of approach. The major concern in the trans-sacral approach is the position of the DSE. It is generally accepted that, in early childhood, the DSE is commonly located at the S2 level, but this level has usually been an approximate estimation with vertebral bodies in the neutral position. Koo et al. [50] discovered cephalad shift of the DSE relative to the vertebral bodies when infants and small children were placed with their hips fully flexed for a caudal block (middle of S2 in the neutral vs. the upper border of S2 in the flexed position, P < 0.001), similar to the findings of an US study by Shin et al. [49]. In the lateral view of the vertebral columns, the spinous processes point downwards compared to the vertebral bodies. As the trans-sacral approach uses the spinous process as a landmark, this will increase the safety margin during puncture. Evaluating the DSE by US before puncture will allow for a safer approach.
Caudal block using the trans-sacral approach is not particularly popular, but the success rate has been reported to be very high (Table 2). In particular, in children aged over 3 years of age, this is a more reliable technique when hiatal identification is difficult [36]. The drug dosage used during block is the same as with the hiatal approach [49].
Recently, regional block using US has become more common in children. Evidence for the advantages of neuraxial block under US guidance in infants and children has been accumulating slower than that for US-guided peripheral nerve block, but US guidance clearly improves safe performance of neuraxial block. Outcome-based prospective and randomized controlled studies are required to prove the benefits of preprocedural US evaluation and US-guided block to establish the usefulness of this technique. In addition, continual education and training are required to improve the performance of these procedures using US guidance.
Fig. 1.
Ultrasound image from L1 to sacrum. CE: cauda equina, CM: conus medullaris, FT: filum terminale, DS: dural sac. *Ligamentum flavum, †dura mater, ‡sacrococcygeal ligament.

Fig. 2.
Ultrasound images at the L2–L3 level in a 6-months-old child. Solid black arrows; ligamentum flavum, dashed arrows; dura mater. SP: spinous process. (A) Triangular epidural space is seen in left transverse plane image. (B) Conus medullaris (CM) at the upper level of L2, spinal nerve roots, and cauda equina fibers are seen in right longitudinal plane image.
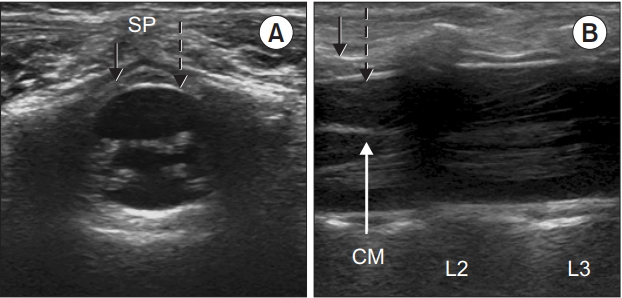
Fig. 3.
Ultrasound images during bolus injection of saline through the epidural needle and following catheter insertion. (A) The black arrow indicates the ligamentum flavums and white arrow indicates the displaced dura mater with drug injection through epidural catheter. (B) The epidural catheter is seen. CM: conus medullaris, DM: dura mater, LF: ligamentum flavum.
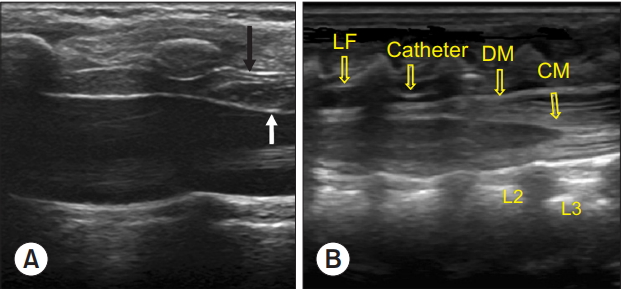
Fig. 4.
Ultrasound images during caudal block in a 6-months-old child. (A) The “frog eye sign” of bilateral sacral cornua (asterisks) and “hump” of the sacrococcygeal ligament (white arrow) are seen in the transverse plane. (B) The anechoic caudal space is seen between the hyperechoic sacrococcygeal ligament (white arrow) and the dorsum of the pelvic surface of the sacrum in the longitudinal plane.

Fig. 5.
Ultrasound images in the transverse planes that match the probe positions in the longitudinal plane. Level 1 shows the widest part of the sacral canal below the sacrococcygeal ligament.
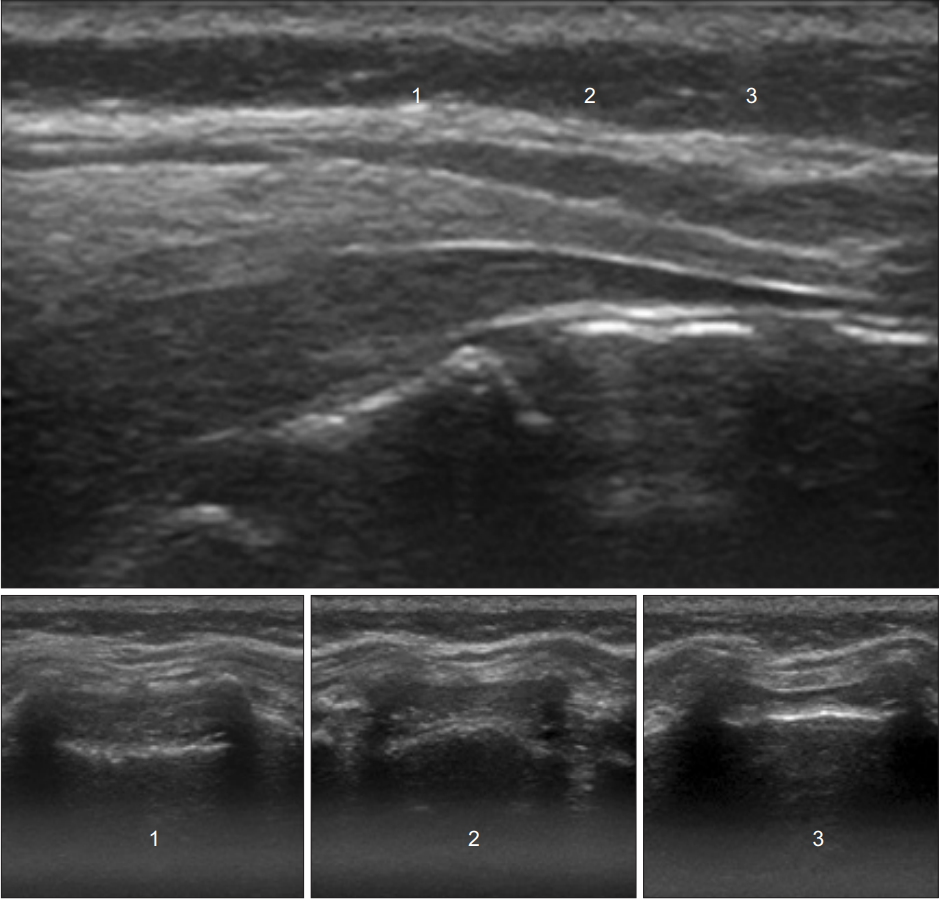
Fig. 6.
The probe positions and ultrasound images during caudal block in an 8-months-old child. (A) The level close to the apex of the sacral hiatus was selected on the transverse view and the needle was placed at the puncture site. (B) Then, the probe was changed to the longitudinal plane and the needle was inserted into the caudal space under ultrasound guidance. (C) The injected solution can be seen within the caudal space (white arrow).
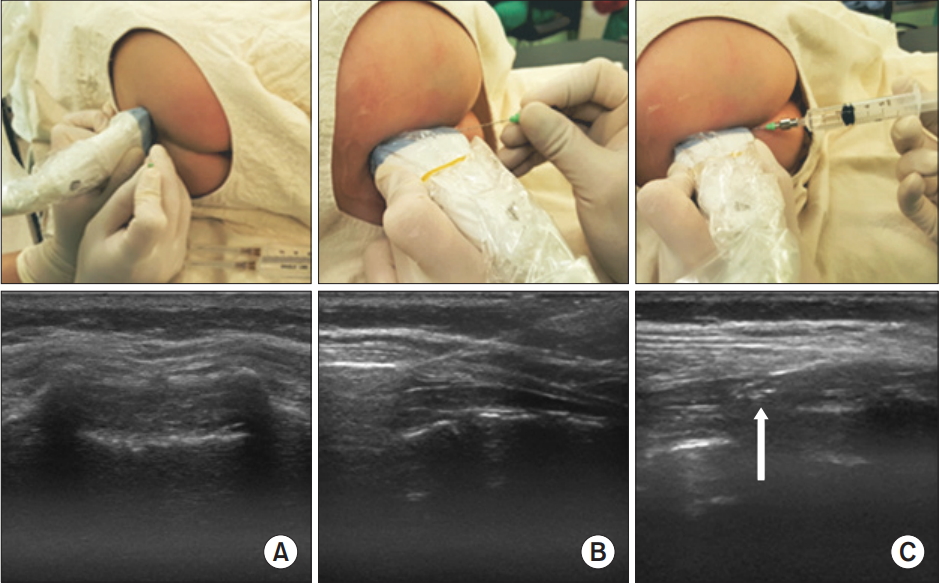
Fig. 7.
Ultrasound images of the caudal area. Solid arrow indicates the needle direction to the space from the S2–S3 intervertebral level (A) and the dashed arrow shows the needle direction through the sacral hiatus (B). Black arrows indicate the point of needle insertions (insets). PSIS: posterior superior iliac spine. *Dural sac end.
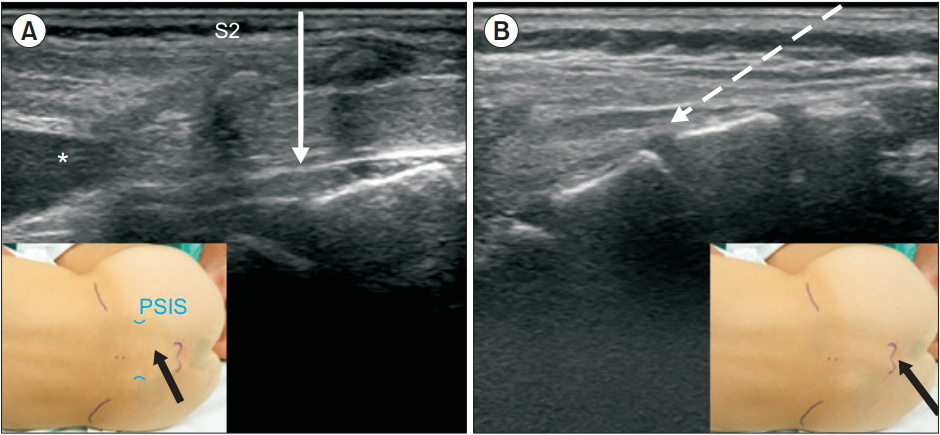
Table 1.
Epidural Puncture Levels for Catheterization and Drug Infusion Rate for Postoperative Analgesia
Bolus 0.05 ml/kg, lock-out 15 minutes. The most common agent used is a combination of 0.125% bupivacaine or 0.15% ropivacaine with fentanyl 2 μg/ml. For abdominal surgery, hydromorphone or morphine, which are more hydrophilic, is recommended because a more cephalad spread is desirable. For thoracic surgery, a more lipophilic opioid is useful to limit the spread. If the catheter tip fails to reach the expected level, hydrophilic opioids are desirable. At age < 3 months, the drug dosage should be halved.
Table 2.
Success Rates of Trans-sacral (S2–S3) Caudal Block in Children
| References | Publication yr. | No. | Success (%) | Dura puncture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Busoni and Sarti [47] | 1987 | 74 | 100 | No |
| Saint-Maurice et al. [51] | 1993 | 46 | 91 | 2 |
| Quinot and Coquelin [52] | 1993 | 11 | 100 | No |
| Kumagai and Yamashita [53] | 1995 | 200 | 96 | No |
| Osaka and Yamashita [54] | 2003 | 551 | 100 | No |
| Shin et al.(ultrasound) [49] | 2009 | 78 | 100 | No |
References
1. Katz J, Seltzer Z. Transition from acute to chronic postsurgical pain: risk factors and protective factors. Expert Rev Neurother 2009; 9: 723-44.


2. Rabbitts JA, Fisher E, Rosenbloom BN, Palermo TM. Prevalence and predictors of chronic postsurgical pain in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pain 2017; 18: 605-14.



3. Ferland CE, Vega E, Ingelmo PM. Acute pain management in children: challenges and recent improvements. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2018; 31: 327-32.


4. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Practice guidelines for acute pain management in the perioperative setting: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Anesthesiology 2012; 116: 248-73.


5. Tsui BC. Ultrasound imaging for regional anesthesia in infants, children, and adolescents: a review of current literature and its application in the practice of neuraxial blocks. Anesthesiology 2010; 112: 719-28.


6. Lam DK, Corry GN, Tsui BC. Evidence for the use of ultrasound imaging in pediatric regional anesthesia: a systematic review. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2016; 41: 229-41.


8. Schulte-Steinberg O. History. Edited by Regional Anaesthesia in Children, Saint-Maurice C, Schulte-Steinberg O: New York, Appleton & Lange. 1990, pp 13-4.
9. Dogliotti AM. Research and clinical observations on spinal anesthesia: with special reference to the peridural technique. Anesth Analg 1933; 12: 59-65.

12. Ruston FG. Epidural anaesthesia in paediatric surgery: present status in the Hamilton general hospital. Can Anaesth Soc J 1964; 11: 12-34.


13. Ecoffey C, Dubousset AM, Samii K. Lumbar and thoracic epidural anesthesia for urologic and upper abdominal surgery in infants and children. Anesthesiology 1986; 65: 87-90.


14. Murat I, Delleur MM, Esteve C, Egu JF, Raynaud P, Saint-Maurice C. Continuous extradural anaesthesia in children. Clinical and haemodynamic implications. Br J Anaesth 1987; 59: 1441-50.


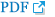
15. Bösenberg AT, Bland BA, Schulte-Steinberg O, Downing JW. Thoracic epidural anesthesia via caudal route in infants. Anesthesiology 1988; 69: 265-9.


16. Chawathe MS, Jones RM, Gildersleve CD, Harrison SK, Morris SJ, Eickmann C. Detection of epidural catheters with ultrasound in children. Paediatr Anaesth 2003; 13: 681-4.


17. Rapp HJ, Folger A, Grau T. Ultrasound-guided epidural catheter insertion in children. Anesth Analg 2005; 101: 333-9.


18. Kil HK, Cho JE, Kim WO, Koo BN, Han SW, Kim JY. Prepuncture ultrasound-measured distance: an accurate reflection of epidural depth in infants and small children. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2007; 32: 102-6.


19. Willschke H, Bosenberg A, Marhofer P, Willschke J, Schwindt J, Weintraud M, et al. Epidural catheter placement in neonates: sonoanatomy and feasibility of ultrasonographic guidance in term and preterm neonates. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2007; 32: 34-40.


20. Tachibana N, Yamauchi M, Sugino S, Watanabe A, Yamakage M. Utility of longitudinal paramedian view of ultrasound imaging for middle thoracic epidural anesthesia in children. J Anesth 2012; 26: 242-5.


21. Suresh S, Long J, Birmingham PK, De Oliveira GS Jr. Are caudal blocks for pain control safe in children? an analysis of 18,650 caudal blocks from the Pediatric Regional Anesthesia Network (PRAN) database. Anesth Analg 2015; 120: 151-6.


22. Dalens B, Hasnaoui A. Caudal anesthesia in pediatric surgery: success rate and adverse effects in 750 consecutive patients. Anesth Analg 1989; 68: 83-9.


23. Veyckemans F, Van Obbergh LJ, Gouverneur JM. Lessons from 1100 pediatric caudal blocks in a teaching hospital. Reg Anesth 1992; 17: 119-25.


24. Wang LZ, Hu XX, Zhang YF, Chang XY. A randomized comparison of caudal block by sacral hiatus injection under ultrasound guidance with traditional sacral canal injection in children. Paediatr Anaesth 2013; 23: 395-400.


25. Ahiskalioglu A, Yayik AM, Ahiskalioglu EO, Ekinci M, Gölboyu BE, Celik EC, et al. Ultrasound-guided versus conventional injection for caudal block in children: a prospective randomized clinical study. J Clin Anesth 2018; 44: 91-6.


26. Ponde VC, Bedekar VV, Desai AP, Puranik KA. Does ultrasound guidance add accuracy to continuous caudal-epidural catheter placements in neonates and infants? Paediatr Anaesth 2017; 27: 1010-4.


27. Johnson SA, Young C, Olney JW. Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the developing brain of nonhypoglycemic mice. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 2008; 20: 21-8.


28. Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber NB, Smith DJ, Martin LD, et al. Ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis in the fetal and neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology 2012; 116: 372-84.



29. Sinner B, Becke K, Engelhard K. General anaesthetics and the developing brain: an overview. Anaesthesia 2014; 69: 1009-22.


31. Houck CS, Vinson AE. Anaesthetic considerations for surgery in newborns. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2017; 102: F359-63.


32. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA review results in new warnings about using general anesthetics and sedation drugs in young children and pregnant women [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2016. Dec 14 [cited 2018 Apr 22]. Available from https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm532356.htm.
33. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA approves label changes for use of general anesthetic and sedation drugs in young children [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2017. Apr 27 [cited 2018 Apr 22]. Available from https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm554634.htm.
34. Ivani G, Suresh S, Ecoffey C, Bosenberg A, Lonnqvist PA, Krane E, et al. The European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy and the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Joint Committee Practice Advisory on Controversial Topics in Pediatric Regional Anesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2015; 40: 526-32.


35. Bogduk N. Clinical Anatomy of Lumbar Spine. 3rd ed. New York, Churchill Livingstone. 1987, pp 63-163.
36. Dalens BJ, Truchon R. Neural blockade for pediatric surgery. Cousins & Bridenbaugh’s Neural Blockade in Clinical Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. 4th ed. Edited by Cousins MJ, Carr DB, Horlocker TT, Bridenbaugh PO: Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a Wolters Kluwer business. 2009, pp 596-611.
37. Kim YA, Kim JY, Kil HK, Kim EM, Kim MK, Kim HS. Accuracy of the epidural catheter position during the lumbar approach in infants and children: a comparison among L2-3, L3-4, and L4-5 approaches. Korean J Anesthesiol 2010; 58: 458-63.



38. Blanco D, Llamazares J, Rincón R, Ortiz M, Vidal F. Thoracic epidural anesthesia via the lumbar approach in infants and children. Anesthesiology 1996; 84: 1312-6.


39. Tsui BC, Fredrickson M, Suresh S. Pediatric epidural & caudal analgesia & anesthesia. Textbook of Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Management. Edited by Hadzic A: New York, McGraw Hill. 2007, p 739.
40. Marhofer P, Bösenberg A, Sitzwohl C, Willschke H, Wanzel O, Kapral S. Pilot study of neuraxial imaging by ultrasound in infants and children. Paediatr Anaesth 2005; 15: 671-6.


41. Shin S, Kim JY, Kim WO, Kim SH, Kil HK. Ultrasound visibility of spinal structures and local anesthetic spread in children undergoing caudal block. Ultrasound Med Biol 2014; 40: 2630-6.


42. Kil HK, Cho JE, Kim WO, Koo BN, Han SW, Kim JY. Prepuncture ultrasound-measured distance: an accurate reflection of epidural depth in infants and small children. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2007; 32: 102-6.


43. Kil HK, Koo BN, Kim WO. To make epidural catheterization less difficult in infants. Paediatr Anaesth 2006; 16: 1196-7.


44. Koo BN, Hong JY, Song HT, Kim JM, Kil HK. Ultrasonography reveals a high prevalence of lower spinal dysraphism in children with urogenital anomalies. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2012; 56: 624-8.


45. Armitage EN. Caudal block in children. Anaesthesia 1979; 34: 396.
46. Dalens B, Chrysostome Y. Intervertebral epidural anaesthesia in paediatric surgery: success rate and adverse effects in 650 consecutive procedures. Paediatr Anaesth 1991; 1: 107-17.

48. Park JH, Koo BN, Kim JY, Cho JE, Kim WO, Kil HK. Determination of the optimal angle for needle insertion during caudal block in children using ultrasound imaging. Anaesthesia 2006; 61: 946-9.


49. Shin SK, Hong JY, Kim WO, Koo BN, Kim JE, Kil HK. Ultrasound evaluation of the sacral area and comparison of sacral interspinous and hiatal approach for caudal block in children. Anesthesiology 2009; 111: 1135-40.


50. Koo BN, Hong JY, Kim JE, Kil HK. The effect of flexion on the level of termination of the dural sac in paediatric patients. Anaesthesia 2009; 64: 1072-6.


51. Saint-Maurice C, Landais A, Othmani H, Khalloufi M. The trans-sacral route. Can the technique be simplified? Cah Anesthesiol 1993; 41: 235-6.

52. Quinot JF, Coquelin G. Trans-sacral caudal anesthesia in ambulatory practice in infants. Our experience. Cah Anesthesiol 1993; 41: 347-8.










