|
 |
|
|
Abstract
Background
This study compared the preventive effects of ramosetron and ondansetron on postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) in highly susceptible patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy.
Methods
In a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study, a total of 120 highly susceptible women (nonsmokers, those receiving opioid-based IV patient-controlled analgesia [PCA]) undergoing abdominal hysterectomy were included in the study. Patients were divided into 2 groups and each group received either 0.3 mg of ramosetron or 4 mg of ondansetron, IV. All patients received fentanyl-based IV PCA during the 48 h postoperative periods. The incidences of PONV and side effects of 5-HT3 antagonists (headache and dizziness) were assessed at 3 intervals (<2 h, 2-24 h and 24-48 h) postoperatively.
Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) are common problems after general anesthesia. Aside from the unpleasant experience to the patient, PONV poses multiple potential medical risks. Increased intra-abdominal pressure and forceful vomiting jeopardize abdominal suture lines and may risk esophageal rupture. Elevated central venous pressures are known to increase morbidity after ocular, tympanic and intracranial procedures. In addition, the risk of aspirating gastric contents increases with PONV, especially if airway reflexes are impaired [1].
The etiology of PONV after general anesthesia is complex. Apfel et al. [2] reported that the female gender, prior history of motion sickness or PONV, non-smokers and the use of postoperative opioids were the most important predictors for PONV. If 0, 1, 2, 3 or all of these risk factors were present, the incidence of PONV was 10%, 21%, 39%, 61% and 79%, respectively. Currently, 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonists are widely administered to treat or prevent PONV. However, there are considerable differences in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics among the drugs in this class.
In this study, we compared the preventive anti-emetic efficacy for commonly used 5-HT3 antagonists, ramosetron and ondansetron, in highly susceptible patients (females, non-smokers, those receiving postoperative opioids) undergoing abdominal hysterectomy.
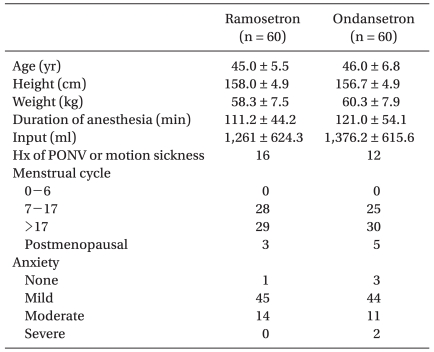
After obtaining approval by the Institutional Review Board at our hospital, written informed consent was obtained for this prospective double-blinded, randomized study of 120 healthy women with American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status classification I or II undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. There were no significant differences in the demographic data (Table 1). Additional inclusion criteria included patients aged 18-60 years having PONV risk factors (i.e non-smokers, use of opioid-based PCA). Exclusion criteria included: history of allergies to any study medication, gastrointestinal disease, insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, administration of anti-emetics or steroids 24 h prior to surgery, active pregnancy, major cardiac or neurological disease and impaired hepatic/renal function.
Patients were randomly allocated to receive either ondansetron (n = 60) or ramosetron (n = 60) by a computerized randomization table. All patients were premedicated with diazepam (10 mg, PO) 1 h before surgery. Upon arrival to the OR, preoperative anxiety was evaluated using a 4 grade scale by an anesthesiologist blinded to the study groups. General anesthesia was induced with propofol (2 mg/kg) and vecuronium (0.1 mg/kg) to facilitate intratracheal intubation. After successful intubation, anesthesia was maintained with 1.0-4.0 vol% sevoflurane and 50% nitrous oxide in oxygen. Ventilation was mechanically controlled and adjusted to maintain an end tidal concentration of CO2 between 35-40 mmHg and the body temperature was maintained at 36 ± 1℃ using an air mattress during surgery. Muscle relaxation was maintained with vecuronium as needed.
At 15 min prior to the end of surgery, patients received either ondansetron (4 mg) or ramosetron (0.3 mg) with fentanyl (50 µg) and ketorolac (30 mg), IV (total volume 4 ml), in addition to being connected to a PCA. Injected drugs were prepared in identically shaped syringes by personnel not involved in the study. The PCA regimen consisted of 800 µg of fentanyl and 180 mg of ketorolac total volume including saline, 100 ml and was programmed to a 2 ml/h basal infusion and 0.5 ml per demand with a 15 min lockout during a 48 h period. If patients complained of persistent nausea/or vomiting and wanted another rescue anti-emetics, metoclopramide was given. A visual analog score was used for postoperative pain evaluation.
All episodes of PONV were recorded through direct questioning by one anesthesiologist blinded to the study group or by complaints from patients during the 3 interval study periods within the first 48 h after anesthesia: 0-2 h, 2-24 h and 24-48 h.
Complete response was defined as no PONV and no requirement for another rescue medication. Nausea was defined as a subjectively unpleasant sensation associated with awareness of the urge to vomit. The adverse effects of the 5-HT3 antagonists such as headache and dizziness were assessed during the study period.
Statistical analyses were performed using a Chi-square test, Fisher exact test and unpaired t-test, as appropriate. A P < 0.05 was considered significant. Values are expressed as means ± SD or number of patients (%). Power analysis was used to determine the number of patients in the study. Based on a preliminary study, a complete response during 48 h after surgery in a patients receiving ondansetron would be 70% and an improvement from 70% to 90% was considered of clinical importance. Based on this assumption, a sample size of 60 in each group was calculated with an α-value of 0.05 and a power (1-β) of 0.8.
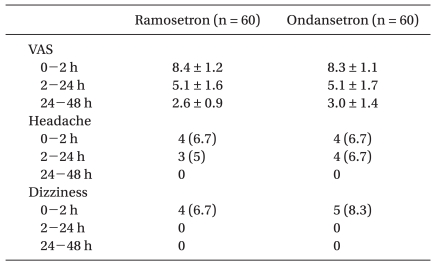
There were no significant differences in preoperative anxiety (Table 1), postoperative pain (VAS) and side effects of the 5-HT3 antagonists such as headache and dizziness (Table 2) between the 2 groups.
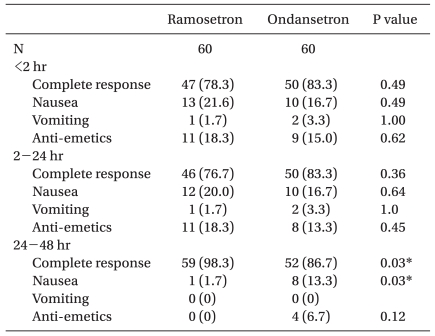
There were no significant differences in complete response, incidence of nausea/vomiting and rescue anti-emetic rescue during < 2 h and 2-24 h postoperatively. A complete response 24-48 h after surgery was significantly higher in the ramosetron group (98.3%) compared with the ondansetron group (86.7%). The incidence of nausea 24-48 h after surgery was significantly lower in the ramosetron group (1.7%) compared with the ondansetron group (13.3%). There was no difference in the use of rescue anti-emetics use during postoperative 24-48 h (ramosetron group, 0% and ondansetron group, 6.7%; Table 3).
We compared the prophylactic anti-emetic efficacy of ramosetron and ondansetron in highly susceptible patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. A single injection of ramosetron (0.3 mg) was more effective than ondansetron (4 mg) in preventing PONV during the 24-48 h period after surgery.
The etiology of PONV after general anesthesia is complex, with the involvement of multiple patient, medical and surgery related factors. The risk factors include female gender, obesity, non-smokers, a history of motion sickness or PONV, menstruation, type of surgical procedure, operation duration, anesthetic technique, postoperative pain and use of opioids [1,3]. From a neurophysiologic point of view, multiple emetic receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, vestibular system, the cerebral cortex and visceral afferents from the gastrointestinal tract are involved in PONV [1,4]. The 5-HT3 receptor antagonists bind competitively to the 5-HT3 receptor in the chemoreceptor trigger zone and gastrointestinal tract to inhibit emetic symptoms [5]. Preoperative anxiety is known to be related with the increase of emesis. α-adrenergic activation by catecholamine release is thought to be related [6] and excessive air swallowing due to anxiety may also contribute.
Ondansetron was the first 5-HT3 receptor antagonist to become clinically available for the treatment and prevention of PONV. However, ondansetron is less selective for the 5-HT3 receptor compared with the other 5-HT3 antagonists. It binds to 5HT1B, 5HT1C α-adrenergic and opioid receptors with low affinity [5]. Systematic review revealed that ondansetron's prophylactic effect on vomiting is good, but the effect on preventing nausea is less pronounced [7].
Ramosetron is a newly developed 5-HT3 receptor antagonist with a higher affinity and longer duration of action compared with other 5-HT3 receptor antagonists [8]. The elimination halflife of ramosetron (9.3 h) is longer than that of ondansetron (3.5 h), grainsetron (4.9 h) and alosetron (3.0 h) [5,8]. Ramosetron has a higher affinity (Ki = 0.091) and slower dissociation rate for 5-HT3 receptors compared with other 5-HT3 receptor antagonists [9]. Also, the active metabolite M1 maintains high receptor occupancy and prolongs action duration [8]. Ayuhara et al. [10] reported that the occupancy of the 5-HT3 receptor correlated with the clinical efficacy of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists.
Multiple studies have reported that ramosetron has a greater or similar effect on prevention of PONV compared with other 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Ramosetron was more effective for preventing nausea and vomiting compared with ondansetron for spinal surgery [11], chemotherapy [12] and total knee replacement surgery [13]. Also, ramosetron was more effective than granisetron in gynecologic surgery [14]. Hahm et al. [13] showed that ramosetron (0.3 mg) was more effective than ondansetron (4 mg) during the 2-48 h postoperative period following total knee replacement. However, in our study, there was a difference of effectiveness only during the 24-48 h post-surgery period. Further, Hahm's study showed a relatively higher incidence of nausea and lower complete response compared with our study although both studies targeted similar character patients (female, non-smoker, use of postoperative opioid use). Hahm's study used spinal anesthesia and epidural hydromorphon PCA. Accordingly, patients showed a relatively higher complete response < 2 h after surgery (83-97%) and became lower (25-50%) over time. Epidural opioids are associated with excellent pain relief but nausea and vomiting are frequent side effects. Eisenach et al. [15] reported an epidural morphine increased the incidence of nausea (50%) and requirement for anti-emetic treatment (30%) compared with intravenous PCA (the incidence of nausea, 30% and the requirement of treatment, 5%). But, because of an inadequate number of patients, they did not show the statistical significance. The emetic effects of epidural opioids are believed to be related to its rostral spread from the lumbar epidural site of injection to the CTZ (chemoreceptor trigger zone) and the vomiting centers. Hydrophilic agents such as morphine and hydromorphon have more rostral spread and higher incidence of nausea and vomiting compared with lipophilic agents such as fentanyl [1]. Different administration sites and physicochemical properties of opioids might partially explain the different results between Hahm's and our study. Relatively low incidence of emetic sequelae in our study might mask the difference of effects between ondansetron and ramosetron.
On the other hand, there were studies reporting similar effects [16,17]. Kim et al. [17] reported that ramosetron (0.3 mg) and ondansetron (8 mg) did not show a the difference in the incidence and severity of PONV during the first 24 h after gynecological surgery. We did not find a difference in effect between drugs in the first 24 h. However, during the postoperative 24-48 h period, ramosetron was more effective than ondansetron. Considering that PCA is usually administrated through the postoperative 48 h period, this finding is thought to have clinical significance. The incidence of PONV in Kim's study (44-50%) was higher compared with our result (17-22%). Different from our study which was limited to abdominal hysterectomy, Kim's study included laparoscopic procedures (48-52%). Gynecologic laparoscopic procedures have been known to induce emesis more frequently [1].
There are several limitations to our study. First, no control group was established. However, because all patients enrolled had several risk factors for PONV which included females, non-smokers, >1 h anesthetic duration, laparotomic surgery and postoperative opioid use, we estimated the incidence of PONV to be approximately 60-70% [2,18]. We thought it would be unethical not to administer any prophylactic antiemetics to establish a control group. A second limitation to our study concerns the dose of ondansetron and ramosetron. Currently, equipotent doses for ondansetron and ramosetron are unknown. Many clinical studies have compared ramosetron at 0.3 mg with ondansetron between 4-16 mg [11-13,16,17]. Previous pharmacokinetic studies used ramosetron at 0.3 mg and ondansetron at 4 mg [9,10]. Ondansetron is known not to have a linear dose response curve. In an animal study, the anti-emetic effects increased until reaching 50 µg/kg but over that, there was a decrease until reaching 100 µg/kg where the effect was increased again with a 500 µg/kg dose [19]. In light of these findings, it is difficult to decide the optimal doses of ramosetron and ondansetron. Third, there are no established parameters to measure nausea severity. The incidence of nausea during 24-48 h period is the important parameter with statistically significant differences in this study. Also, because nausea is a subjective symptom, it is difficult to accurately judge the development of nausea. A validated visual analog scale or a severity grade for nausea is needed to estimate the efficiency of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Lastly, we did not measure the doses of consumed fentanyl during the study periods. Opioid in PCA is a critical factor in developing delayed PONV. Accordingly, comparing opioid consumption for the exact evaluation of effect on 5-HT3 receptor antagonists may be needed.
In conclusion, ramosetron at 0.3 mg is more effective in preventing delayed PONV in highly susceptible women undergoing abdominal hysterectomy compared with ondansetron (4 mg).
References
1. Watcha MF, White PF. Postoperative nausea and vomiting. Its etiology, treatment and prevention. Anesthesiology 1992; 77: 162-184. PMID: 1609990.


2. Apfel CC, Läärä E, Koivuranta M, Greim CA, Roewer N. A simplified risk score for predicting postoperative nausea and vomiting: conclusions from cross-validations between two centers. Anesthesiology 1999; 91: 693-700. PMID: 10485781.


3. Sinclair DR, Chung F, Mezei G. Can postoperative nausea and vomiting be predicted? Anesthesiology 1999; 91: 109-118. PMID: 10422935.


4. Kovac AL. Prevention and treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Drugs 2000; 59: 213-243. PMID: 10730546.


5. Gan TJ. Selective serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonists for postoperative nausea and vomiting: are they all the same? CNS Drugs 2005; 19: 225-238. PMID: 15740177.


6. Jenkins LC, Lahay D. Central mechanisms of vomiting related to catecholamine response: anaesthetic implication. Can Anaesth Soc J 1971; 18: 434-441. PMID: 5156318.


7. Tramèr MR, Reynolds DJ, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Efficacy, dose-response, and safety of ondansetron in prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a quantitative systematic review of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Anesthesiology 1997; 87: 1277-1289. PMID: 9416710.


8. Rabasseda X. Ramosetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist for the control of nausea and vomiting. Drugs Today (Barc) 2002; 38: 75-89. PMID: 12532186.


9. Hirata T, Keto Y, Funatsu T, Akuzawa S, Sasamata M. Evaluation of the pharmacological profile of ramosetron, a novel therapeutic agent for irritable bowel syndrome. J Pharmacol Sci 2007; 104: 263-273. PMID: 17652911.


10. Ayuhara H, Takayanagi R, Okuyama K, Yoshimoto K, Ozeki T, Yokoyama H, et al. Receptor occupancy theory-based analysis of interindividual differences in antiemetic effects of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Int J Clin Oncol 2009; 14: 518-524. PMID: 19967488.


11. Choi YS, Shim JK, Yoon DH, Jeon DH, Lee JY, Kwak YL. Effect of ramosetron on patient-controlled analgesia related nausea and vomiting after spine surgery in highly susceptible patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008; 33: E602-E606. PMID: 18670328.


12. Shi Y, He X, Yang S, Ai B, Zhang C, Huang D, et al. Ramosetron versus ondansetron in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal side effects: A prospective randomized controlled study. Chemotherapy 2007; 53: 44-50. PMID: 17202811.


13. Hahm TS, Ko JS, Choi SJ, Gwak MS. Comparison of the prophylactic anti-emetic efficacy of ramosetron and ondansetron in patients at high-risk for postoperative nausea and vomiting after total knee replacement. Anaesthesia 2010; 65: 500-504. PMID: 20337618.


14. Fujii Y, Saitoh Y, Tanaka H, Toyooka H. Comparison of ramosetron and granisetron for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting after gynecologic surgery. Anesth Analg 1999; 89: 476-479. PMID: 10439770.


15. Eisenach JC, Grice SC, Dewan DM. Patients-controlled analgesia following cesarean section: A comparison with epidural and intramuscular narcotics. Anesthesiology 1988; 68: 444-448. PMID: 3345002.


16. Ryu J, So YM, Hwang J, Do SH. Ramosetron versus ondansetron for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc 2010; 24: 812-817. PMID: 19707823.


17. Kim SI, Kim SC, Baek YH, Ok SY, Kim SH. Comparison of ramosetron with ondansetron for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing gynaecological surgery. Br J Anaesth 2009; 103: 549-553. PMID: 19700442.


18. Pan PH, Lee SC, Harris LC. Antiemetic prophylaxis for postdischarge nausea and vomiting and impact on functional quality of living during recovery in patients with high emetic risks: A prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of two prophylactic antiemetic regimens. Anesth Analg 2008; 107: 429-438. PMID: 18633020.


19. Andrews PL, Bhandari P, Davey PT, Bingham S, Marr HE, Blower PR. Are all 5-HT3 receptor antagonists the same? Eur J Cancer 1992; 28A(Suppl 1): S2-S6. PMID: 1320915.

- TOOLS