1. Gan TJ, Belani KG, Bergese S, Chung F, Diemunsch P, Habib AS, et al. Fourth consensus guidelines for the management of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesth Analg 2020; 131: 411-48.


3. Ishii K, Makita T, Yamashita H, Matsunaga S, Akiyama D, Toba K, et al. Total intravenous anesthesia with propofol is associated with a lower rate of postoperative delirium in comparison with sevoflurane anesthesia in elderly patients. J Clin Anesth 2016; 33: 428-31.


5. Hasselager RP, Hallas J, G├Čgenur I. Inhalation or total intravenous anaesthesia and recurrence after colorectal cancer surgery: a propensity score matched Danish registry-based study. Br J Anaesth 2021; 126: 921-30.


8. Grant MC, Pio Roda CM, Canner JK, Sommer P, Galante D, Hobson D, et al. The impact of anesthesia-influenced process measure compliance on length of stay: results from an enhanced recovery after surgery for colorectal surgery cohort. Anesth Analg 2019; 128: 68-74.


9. Yoon S, Joo H, Oh YM, Lee J, Bahk JH, Lee HJ. Validation and clinical utility of the Korean version of the Quality of Recovery-15 with enhanced recovery after surgery: a prospective observational cohort study. Br J Anaesth 2020; 125: 614-21.


11. Myles PS. Measuring quality of recovery in perioperative clinical trials. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2018; 31: 396-401.


12. Myles PS, Boney O, Botti M, Cyna AM, Gan TJ, Jensen MP, et al. Systematic review and consensus definitions for the standardised endpoints in perioperative medicine (StEP) initiative: patient comfort. Br J Anaesth 2018; 120: 705-11.


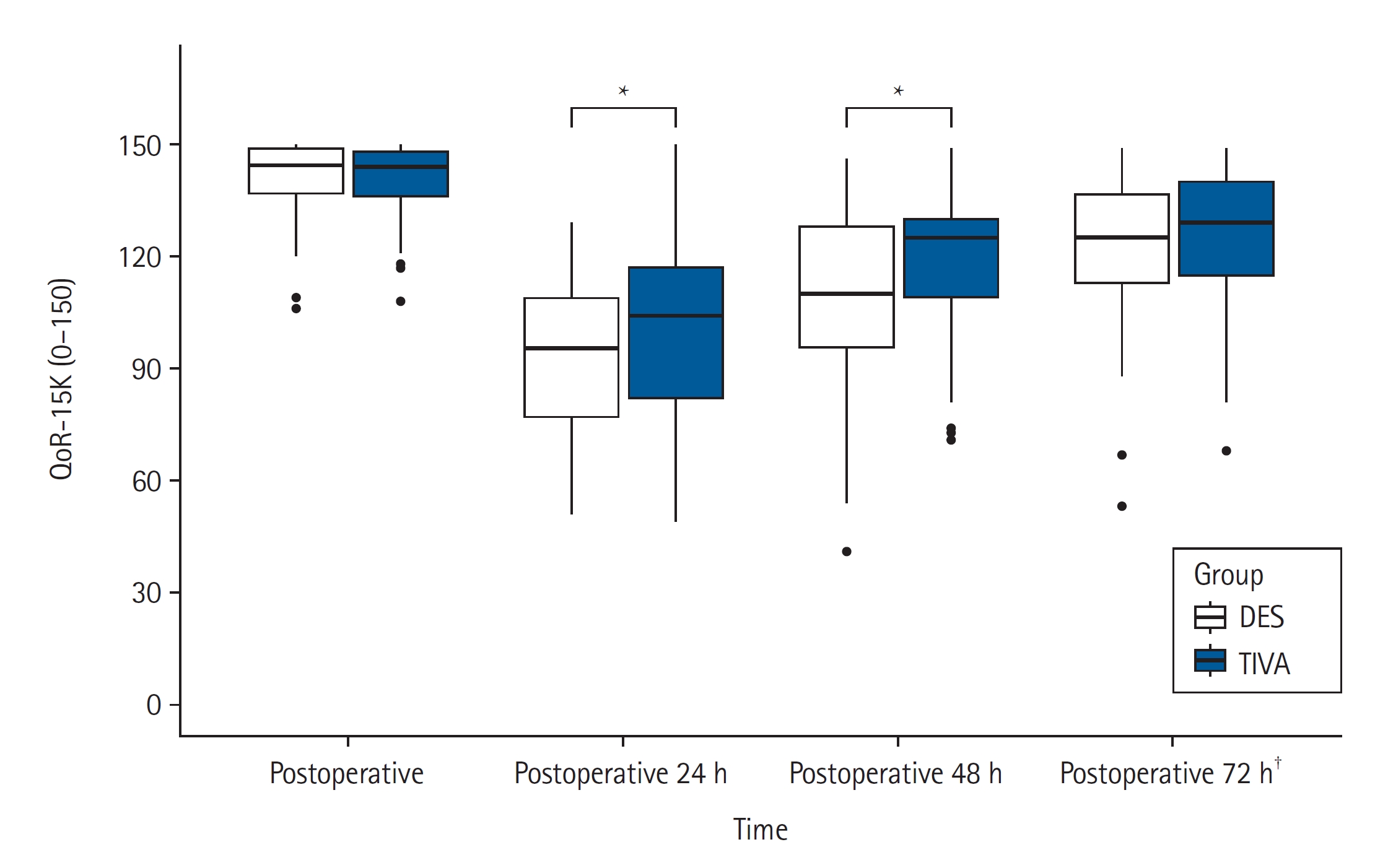
13. Kleif J, Waage J, Christensen KB, G├Čgenur I. Systematic review of the QoR-15 score, a patient- reported outcome measure measuring quality of recovery after surgery and anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 2018; 120: 28-36.


17. Apfel CC, L├ż├żr├ż E, Koivuranta M, Greim CA, Roewer N. A simplified risk score for predicting postoperative nausea and vomiting: conclusions from cross-validations between two centers. Anesthesiology 1999; 91: 693-700.


19. Thomas ME, Blaine C, Dawnay A, Devonald MA, Ftouh S, Laing C, et al. The definition of acute kidney injury and its use in practice. Kidney Int 2015; 87: 62-73.


20. Barrington MJ, Seah GJ, Gotmaker R, Lim D, Byrne K. Quality of recovery after breast surgery: a multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing pectoral nerves interfascial plane (pectoral nerves II) block with surgical infiltration. Anesth Analg 2020; 130: 1559-67.

22. Lee WK, Kim MS, Kang SW, Kim S, Lee JR. Type of anaesthesia and patient quality of recovery: a randomized trial comparing propofol-remifentanil total i.v. anaesthesia with desflurane anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 2015; 114: 663-8.


26. De Oliveira GS Jr, Bialek J, Rodes ME, Kendall MC, McCarthy RJ. The effect of sevoflurane compared to propofol maintenance on post-surgical quality of recovery in patients undergoing an ambulatory gynecological surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, controlled, clinical trial. J Clin Anesth 2017; 43: 70-4.


28. Niu Z, Gao X, Shi Z, Liu T, Wang M, Guo L, Qi D. Effect of total intravenous anesthesia or inhalation anesthesia on postoperative quality of recovery in patients undergoing total laparoscopic hysterectomy: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth 2021; 73: 110374.


31. Stark PA, Myles PS, Burke JA. Development and psychometric evaluation of a postoperative quality of recovery score: the QoR-15. Anesthesiology 2013; 118: 1332-40.


32. Shin SW, Cho AR, Lee HJ, Kim HJ, Byeon GJ, Yoon JW, et al. Maintenance anaesthetics during remifentanil-based anaesthesia might affect postoperative pain control after breast cancer surgery. Br J Anaesth 2010; 105: 661-7.


33. Peng K, Liu HY, Wu SR, Liu H, Zhang ZC, Ji FH. Does propofol anesthesia lead to less postoperative pain compared with inhalational anesthesia?: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth Analg 2016; 123: 846-58.


35. Dam M, Hansen C, Poulsen TD, Azawi NH, Laier GH, Wolmarans M, et al. Transmuscular quadratus lumborum block reduces opioid consumption and prolongs time to first opioid demand after laparoscopic nephrectomy. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2021; 46: 18-24.


38. Ryu KH, Hwang SH, Shim JG, Ahn JH, Cho EA, Lee SH, et al. Comparison of vasodilatory properties between desflurane and sevoflurane using perfusion index: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Anaesth 2020; 125: 935-42.