|
 |
| Korean J Anesthesiol > Volume 74(2); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Dexmedetomidine, an alpha-2 agonist, has been used for attenuation of hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy but not through the nebulized route. We evaluated the effects of preoperative dexmedetomidine nebulization on the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation and examined the intraoperative anesthetic-analgesic requirements and recovery outcomes.
Methods
Overall, 120 American Society of Anesthesiologists I & II adult patients (of either gender) undergoing elective surgeries and requiring tracheal intubation, were randomized to receive nebulized dexmedetomidine (1 µg/kg in 3–4 ml of 0.9% saline) or 0.9% saline (3–4 ml), 30 min before anesthesia induction. Heart rate (HR) and non-invasive systolic blood pressure (SBP) were monitored for 10 min following laryngoscopy.
Results
After laryngoscopy, linear mixed effect modelling showed significantly lower trend of increase in HR in the dexmedetomidine group versus saline (P = 0.012); however, there was no difference in the SBP changes between the two groups (P = 0.904). Induction dose of propofol (P < 0.001), intraoperative fentanyl consumption (P = 0.007), and isoflurane requirements (P = 0.013) were significantly lower in the dexmedetomidine group. There was no difference in the 2 h incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) (P = 0.612) or sore-throat (P = 0.741).
Conclusions
Nebulized dexmedetomidine at 1 µg/kg attenuated the increase in HR but not SBP following laryngoscopy and reduced the intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic consumption. There was no effect on early PONV, sore-throat, or increase in incidence of adverse effects. Nebulized dexmedetomidine may represent a favorable alternative to the intravenous route in short duration surgeries.
Direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation following induction of anesthesia are associated with hemodynamic changes due to increased sympathoadrenal activity, which may result in hypertension and/or tachycardia [1,2]. Although transient, this exaggerated response may precipitate hypertensive crises, myocardial ischemia, arrhythmias, or increases in intracranial pressure in susceptible individuals [1]. Various drugs—including local anesthetics, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and narcotic analgesics—have been tried to blunt the laryngoscopy and intubation response, with varied success [3–9].
Dexmedetomidine is a potent and highly selective alpha-2 receptor agonist with sympatholytic, sedative, amnestic, and analgesic properties [10]. Its pleiotropic effects have led to its increasing use for reducing anesthetic and analgesic requirements in the perioperative period [10]. The efficacy of dexmedetomidine in decreasing the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation has been studied through intravenous [11–15], intranasal [16,17], and intramuscular routes [18]. However, intravenous administration may cause bradycardia and hypotension, and intranasal administration may be associated with irritation [19].
Nebulized dexmedetomidine, administered in doses of 1 and 2 µg/kg has been found to be an effective premedication in pediatric patients [19,20]. Nebulized dexmedetomidine may offer an attractive alternative to both intravenous as well as intranasal routes of administration because drug deposition following nebulization takes place over nasal, buccal, as well as respiratory mucosa [19,20]. To the best of our knowledge, there are no studies demonstrating the effects of nebulized dexmedetomidine on the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation.
Thus, the primary aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of preoperative dexmedetomidine nebulization (1 µg/kg) on the heart rate (HR) response to laryngoscopy and intubation in adult patients. The secondary aims were to evaluate the effects of nebulized dexmedetomidine on the systolic blood pressure (SBP) response following laryngoscopy and intubation, intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic consumption, time to extubation, and the 2-h incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) and sore throat.
The study was designed as a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, parallel arm clinical trial.
The study subjects were adult patients (18–60 year) of either gender who were classified as American Society of Anesthesiologists grade I or II. All subjects were scheduled for elective short-duration, non-cardiac, non-neurosurgical operations requiring general anesthesia and tracheal intubation.
The Institutional Ethics Committee approved the study (T/IM-NF/Anaesth/18/44), and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. The study was registered prospectively in the Clinical Trials Registry of India (CTRI) (trial registration number: CTRI/2019/01/017060, trial registration date: 14/01/2019, Principal Investigator: Dr. Satyajeet Misra). This clinical research was done following the ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration 2013.
We excluded from the study patients undergoing emergency surgeries, obese individuals (body mass index > 30 kg/m2), patients with known or unanticipated difficult intubation and those requiring more than 15 s or two attempts at laryngoscopy, patients with heart rhythms other than sinus, patients with known allergy to dexmedetomidine, and those on anti-hypertensive medications or preoperative drugs that could be potential confounders (clonidine, gabapentin, pregabalin, steroids).
Patients were assigned to two equal groups by generating randomization codes using a simple randomization software.
Group 1 (saline) patients received 0.9% saline nebulization (3–4 ml), 30 min before induction of anesthesia.
Group 2 (dexmedetomidine) patients received 1 µg/kg dexmedetomidine nebulization diluted in 3–4 ml of 0.9% saline, 30 min before induction of anesthesia.
Allocation concealment was achieved with the use of sealed opaque envelopes that were opened once patients were received in the preoperative holding area on the day of surgery.
The drugs for nebulization (saline or dexmedetomidine) were prepared and administered by an independent investigator in the preoperative holding area. Nebulization was carried out with an electrical compressor nebulizer (Eco Smart, Saify Healthcare and Medi Devices, India), capable of creating a fine mist, until the entire volume was dispersed–usually within 15–20 min. Nebulization was stopped when there was no further mist on tapping the volume chamber. The investigator oversaw the entire nebulization procedure and—while taking no further part in the study—was authorized to intervene if a patient developed bradycardia or experienced increased sedation or decreases in peripheral oxygen saturation. In such an event, the nebulization was to be stopped and the patient treated accordingly.
After premedication with 4 mg intravenous ondansetron, 1 mg midazolam, and 2 µg/kg fentanyl. induction of anesthesia was carried out with 10 mg bolus aliquots of propofol titrated to loss of verbal response. After achieving adequate bag mask ventilation, the patient was paralyzed with an intubating dose of inj. vecuronium bromide (0.15 mg/kg). Depth of anesthesia was achieved with isoflurane in 50% air-oxygen mixture to maintain bi-spectral index (BIS; BIS Quatro, Covidien, USA) of 50–60; BIS sensors were applied before anesthesia induction. Ventilation was adjusted to maintain end-tidal carbon-dioxide at 32–35 mmHg.
Administration of additional doses of fentanyl were to be given if an increase in HR and/or SBP greater than 20% of the pre-induction baseline occurred during the surgery. Fluids were administered according to the orders of the attending physician.
The investigators who carried out the laryngoscopy and intubation each have more than 10 years of experience in anesthetic practice. Increases in blood pressure (BP) in the 10-min interval following laryngoscopy and intubation were treated with small aliquots of propofol (20–30 mg), while decreases in BP and HR were treated with inj. ephedrine (6 mg) and inj. atropine (0.6 mg), respectively.
Following surgery, neuromuscular blockade was antagonized with inj. neostigmine (0.05 mg/kg) and inj. glycopyrrolate (0.02 mg/kg). The trachea was extubated once the patient was able to follow verbal commands. Patients were kept in the postoperative care unit for an additional 3 h and discharged to the ward once they met the criteria for discharge.
The primary aim was to study the HR changes following laryngoscopy and intubation in the two groups and, accordingly, HR was measured at various time points: before administration of nebulization, after nebulization but before induction (baseline), and at every 1-min interval until 10 min after laryngoscopy.
The secondary aim was to study the non-invasive SBP changes following laryngoscopy and intubation, intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic consumption, time to extubation, and the 2-h incidence of PONV and sore-throat. BP measurements were performed at the same time points as the HR. The induction dose of propofol, total dose of intraoperative fentanyl and mean minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of isoflurane were recorded for each patient. The response to skin incision was noted and recorded as a binary ‘yes/no response’ (no, if < 20% changes in HR and/or SBP; yes, if > 20% changes in HR and/or SBP). If a positive response to skin incision was present, inj. fentanyl (1 µg/kg) was repeated. The time to extubation in minutes (from administration of neostigmine to removal of the tracheal tube) was noted in both the groups. The peripheral oxygen saturation and sedation scores (modified observer’s assessment of alertness/sedation scale) [21] were also recorded before and after nebulization for each patient.
PONV (subjective feeling of the urge to vomit or retching and/or vomiting) was assessed at 2 h after surgery. Similarly, postoperative sore-throat (subjective feeling of irritation, discomfort or lump or pain in throat) was evaluated at 2 h after surgery, when patients would have recovered from the effects of anesthetic agents. Both of these effects were recorded as present or absent, but their severity was not assessed. All the outcome parameters were recorded by the investigator(s) in charge of the case.
Assuming that there would be a 20% difference in the maximum HR between the two groups following laryngoscopy, 50 patients in each group were required to power the study to 80% to detect the difference with an alpha error of 5% (two-tailed). The assumed pooled standard deviation was 35. Accounting for 20% drop-outs after recruitment (unanticipated difficult intubation; laryngoscopy requiring more than 15 seconds or two attempts; protocol violation), we aimed to recruit 120 patients for the study. Continuous variables were expressed as means ± SD, and categorical variables were expressed as proportions. Linear mixed effect modelling was performed to test the difference in the trend of repeated measures; i.e., HR and SBP. The difference in continuous variables were analyzed with independent t-test, and categorical variables were tested with the Chi-square test or the Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. Statistical analyses were performed with R 3.5 (R foundation, Austria).
A total of 120 patients were enrolled in the study over a one-year period (study start date: January 1, 2019; end date: January 9, 2020; Fig. 1, consort diagram). We did not encounter any attrition (drop-out) after patient enrollment due to unanticipated difficult intubation, repeated or prolonged laryngoscopy or protocol violation. Patient demographics are presented in Table 1. Surgeries were mostly short duration, approximately 2–3 h (modified radical mastectomies, laparoscopic cholecystectomies, ileostomy closures, laparoscopic hysterectomies, etc.).
Following nebulization, there were no differences in the pre-induction hemodynamics or sedation scores between the two groups. After laryngoscopy and intubation, linear mixed effect modelling showed a significantly lower trend of increase in HR in the dexmedetomidine group versus the saline group (P = 0.012, Fig. 2). However, there was no significant difference in the SBP response between the two groups (P = 0.904, Fig. 3). The induction dose of propofol, consumption of intraoperative fentanyl, and the mean isoflurane requirements were significantly less in the dexmedetomidine group versus the saline group (Table 2). Similarly, there was a significant difference in the skin incision response, with a more positive response to skin incision seen in the saline group (Table 2). There was no difference in the time to extubation, incidence of PONV, or sore-throat between the two groups (Table 2). There were no adverse events related to dexmedetomidine nebulization, such as intra- or postoperative bradycardia and hypotension.
We found a significant effect of preoperative dexmedetomidine nebulization (1 µg/kg) versus saline treatment on the HR responses following laryngoscopy and intubation. Preoperative dexmedetomidine nebulization was also effective in reducing the intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic consumption. However, there was no effect of dexmedetomidine nebulization on the SBP responses following laryngoscopy or on the incidence of early PONV or postoperative sore-throat.
Common reasons for the hemodynamic changes following laryngoscopy and intubation are elevation of epiglottis, difficulty in glottic visualization, displacement of tongue, duration of laryngoscopy, and insertion of the tracheal tube [22]. Dexmedetomidine acts on various brain stem and medullary nuclei (nucleus tractus solitarus, lateral reticular nucleus) and the hypothalamus to decrease the sympathetic nervous activity and attenuate the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation [23].
Various studies have investigated the effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation [11–15,23–26]. While doses of 1–2 µg/kg have been found to be effective in attenuating this hemodynamic response, they are associated with significant side effects, such as bradycardia, hypotension, or respiratory depression [24,25]. Lawrence and De Lange [24], found that a single dose of 2 µg/kg dexmedetomidine caused a higher incidence of bradycardia and hypotension compared with the placebo treatment. Similarly, Mahajan et al. [25], found that with the same depth of anesthesia, there was a significant fall in HR and SBP and DBP in the dexmedetomidine group (1 µg/kg) versus the placebo group, and that this effect lasted until 30 min following drug administration.
Our results differ from those of previous studies [24,25]. Although we found that the increase in HR was significantly attenuated in the dexmedetomidine group versus saline following laryngoscopy, we did not find any incidence of bradycardia. Additionally, there was no significant difference in the SBP increases following laryngoscopy between the two groups. This can be explained by our route of administration. The bio-availability of dexmedetomidine via inhalation is 65% through nasal mucosa and 82% through buccal mucosa [19]. This may be comparable to 0.5 µg/kg of an intravenous dose [17], and as previous studies have shown, such doses only have a modest effect on hemodynamics following laryngoscopy and intubation [15,23]. Further reasons for a lack of effect of nebulized dexmedetomidine versus saline on the SBP changes following laryngoscopy could be that since the depth of anesthesia was similar in both groups, a higher MAC of isoflurane in the saline group versus a lower MAC in the dexmedetomidine group may have led to similar BP changes.
In the present study, nebulized dexmedetomidine reduced the induction dose of propofol as well as the intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic consumption. Although the duration of surgery was similar in both groups, a significantly lower consumption of fentanyl was seen in the dexmedetomidine group, despite patients undergoing a variety of surgeries. In addition, we also noted a significant difference in the response to skin incision between the groups, which may have been related to a better quality of analgesia in the dexmedetomidine group. Thus, the effects of nebulized dexmedetomidine is similar to those of intravenous dexmedetomidine on the intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic consumption [14,24,26].
Unlike Lawrence and De Lange [24], who found a significant effect of 2 µg/kg intravenous dexmedetomidine on baseline sedation, we found that the levels of sedation following nebulization and before induction of anesthesia were not different from the baseline values in either of the two groups. This may be related to the dose of dexmedetomidine used in our study and the patient population studied. While Abdel-Ghaffar et al. [20] found good sedation with 2 µg/kg nebulized dexmedetomidine in pre-school children undergoing bone marrow biopsy, Zanaty and El Metainy [19], found that in children undergoing outpatient dental surgery, doses of 1 µg/kg nebulized dexmedetomidine provided lower levels of sedation as compared to nebulized ketamine or a combination (1 µg/kg dexmedetomidine + 1 mg ketamine). Thus, a higher dose of nebulized dexmedetomidine may be required to achieve optimal sedation in adults.
While some studies have shown that supplemental dexmedetomidine administration was effective in reducing early PONV [27], other researchers have found a beneficial effect of supplemental dexmedetomidine on early nausea but not vomiting [28]. The reduction in PONV due to dexmedetomidine may be due to an opioid sparing action, a sympatholytic effect, or a direct antiemetic effect by activation of alpha-2 adrenoreceptors [28]. In our study, however, there was no significant difference in the early PONV between the two groups, despite a lower consumption of fentanyl in the dexmedetomidine group. Several reasons may have contributed to this lack of significant difference. Our anesthetic protocol included pre-induction administration of ondansetron, the effects of which is expected to last 8 h and thus may have masked any effect of dexmedetomidine on early PONV, since the surgeries were typically of short duration. Additionally, in most of the studies that have demonstrated an effect of dexmedetomidine on PONV, dexmedetomidine was either administered as a bolus dose at the end of surgery [27] or as continuous infusion [28], whereas we only administered a single dose before induction of anesthesia. Finally, the surgeries performed on the subjects in our study were mixed in nature, which may have also impacted the incidence of PONV.
The incidence of postoperative sore throat following tracheal intubation is 21–65% [29], and ranks as the eighth most adverse event in the postoperative period [30]. Previous reports have described the favorable effects of dexmedetomidine on dilatation of bronchi by relaxation of smooth muscles secondary to a direct effect on peripheral alpha-2 adrenoreceptors [31]; thus, we sought to investigate whether there is an effect of dexmedetomidine on the incidence of postoperative sore throat. However, we did not find a beneficial effect of nebulized dexmedetomidine on postoperative sore throat.
No previous studies have evaluated the effects of dexmedetomidine administered via the nebulized route on the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation, intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic requirements, and other postoperative outcomes. Instead of using traditional statistical measures (e.g., analysis of variance) to test for the difference in hemodynamic parameters which estimates fixed effects, we utilized the mixed effect modelling for repeated measures (which tests for both fixed and random effects) since the BP or HR at any given minute may be the function of the previous reading.
We evaluated a single dose of nebulized dexmedetomidine and are thus unable to comment whether different doses will have different effects on hemodynamics. In addition, we did not use a comparator intravenous arm, which would have allowed us to compare the nebulized route of administration with the systemic route, but with the objective of finding better routes of administration, systemic administration may be avoided, especially in short duration surgeries.
In conclusion, a single dose of nebulized dexmedetomidine at 1 µg/kg, administered 30 min before induction of anesthesia, significantly attenuated the increase in HR but not SBP after laryngoscopy and decreased the intraoperative anesthetic and analgesic consumption (compared to the saline treatment) without an increase in adverse effects. Nebulized dexmedetomidine may represent a favorable alternative to the intravenous route in adult patients undergoing short-duration surgeries.
NOTES
Author Contributions
Satyajeet Misra (Conceptualization; Data curation; Investigation; Methodology; Project administration; Resources; Supervision; Validation; Writing – original draft; Writing – review & editing)
Bikram Kishore Behera (Data curation; Formal analysis; Investigation; Resources; Validation; Writing – review & editing)
Jayanta Kumar Mitra (Data curation; Investigation; Resources; Writing – review & editing)
Alok Kumar Sahoo (Data curation; Investigation; Supervision; Writing – review & editing)
Sritam Swarup Jena (Data curation; Investigation; Supervision; Writing – review & editing)
Anand Srinivasan (Data curation; Formal analysis; Methodology; Software; Validation; Writing – review & editing)
Fig. 2.
Changes in heart rate (HR) in the dexmedetomidine group and the saline group. Baseline represents the post-nebulization pre-induction period. Mixed effect modelling showed a significantly lower trend of increase in HR in the dexmedetomidine group versus saline (P = 0.012). Vertical bars represent standard error of the mean.
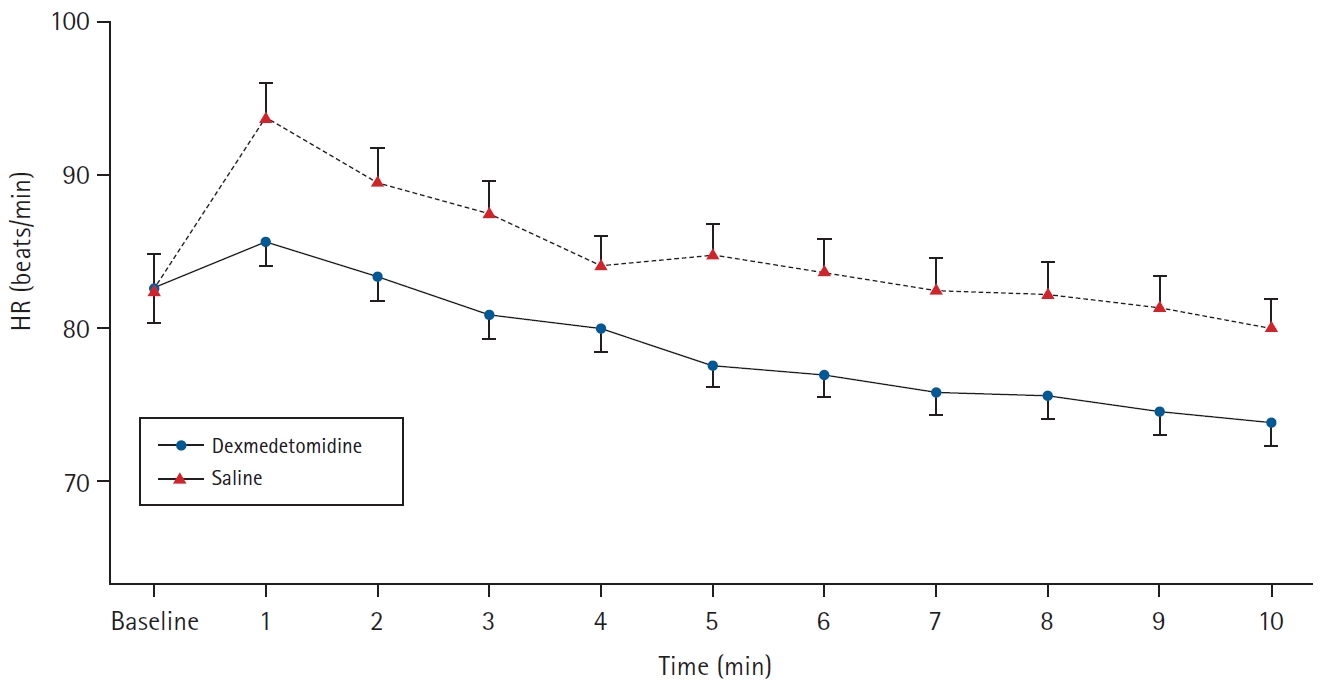
Fig. 3.
Changes in systolic blood pressure (SBP) in the dexmedetomidine group and the saline group. Baseline represents the post-nebulization preinduction period. Mixed effect modelling showed no difference between the two groups in the overall trend in the SBP changes during the study period (P = 0.904). Vertical bars represent standard error of the mean.
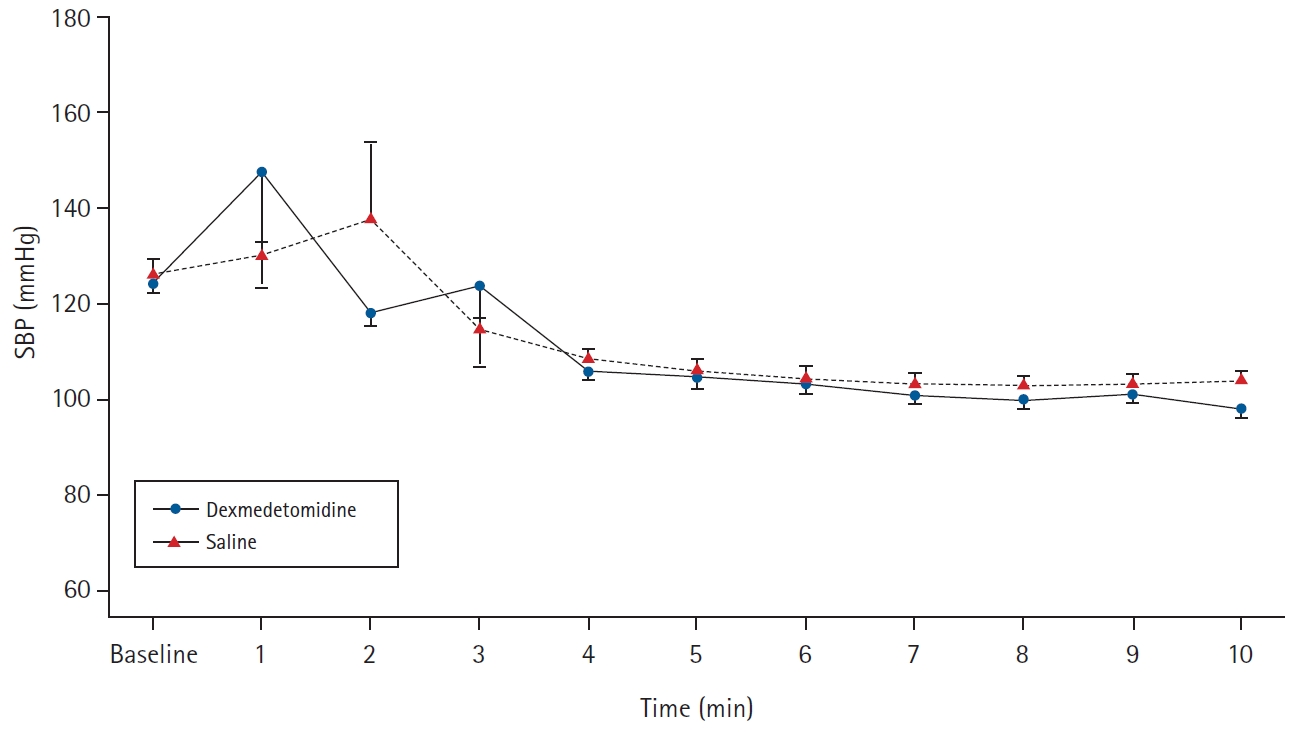
Table 1.
Patient Demographics
Table 2.
Secondary Outcomes
References
1. Kovac AL. Controlling the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation. J Clin Anesth 1996; 8: 63-79.


2. Edwards ND, Alford AM, Dobson PM, Peacock JE, Reilly CS. Myocardial ischaemia during tracheal intubation and extubation. Br J Anaesth 1994; 73: 537-9.


3. Victory RA, Gajraj NM, Pace NA, Ostman LP, White PF. Nebulized bupivacaine attenuates the heart rate response following tracheal intubation. J Clin Anesth 1995; 7: 9-13.


4. Singh H, Vichitvejpaisal P, Gaines GY, White PF. Comparative effects of lidocaine, esmolol, and nitroglycerin in modifying the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation. J Clin Anesth 1995; 7: 5-8.


5. Inada E, Cullen DJ, Nemeskal AR, Teplick R. Effect of labetalol or lidocaine on the hemodynamic response to intubation: a controlled randomized double-blind study. J Clin Anesth 1989; 1: 207-13.


6. Ghignone M, Quintin L, Duke PC, Kehler CH, Calvillo O. Effects of clonidine on narcotic requirements and hemodynamic response during induction of fentanyl anesthesia and endotracheal intubation. Anesthesiology 1986; 64: 36-42.


7. Charuluxananan S, Kyokong O, Somboonviboon W, Balmongkon B, Chaisomboonpan S. Nicardipine versus lidocaine for attenuating the cardiovascular response to endotracheal intubation. J Anesth 2000; 14: 77-81.


8. Kutlesic MS, Kutlesic RM, Mostic-Ilic T. Attenuation of cardiovascular stress response to endotracheal intubation by the use of remifentanil in patients undergoing Cesarean delivery. J Anesth 2016; 30: 274-83.


9. Min JH, Chai HS, Kim YH, Chae YK, Choi SS, Lee A, et al. Attenuation of hemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation during rapid sequence induction: remifentanil vs. lidocaine with esmolol. Minerva Anestesiol 2010; 76: 188-92.

10. Afonso J, Reis F. Dexmedetomidine: current role in anesthesia and intensive care. Rev Bras Anestesiol 2012; 62: 118-33.


11. El-Shmaa NS, El-Baradey GF. The efficacy of labetalol vs dexmedetomidine for attenuation of hemodynamic stress response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation. J Clin Anesth 2016; 31: 267-73.


12. Kunisawa T, Nagata O, Nagashima M, Mitamura S, Ueno M, Suzuki A, et al. Dexmedetomidine suppresses the decrease in blood pressure during anesthetic induction and blunts the cardiovascular response to tracheal intubation. J Clin Anesth 2009; 21: 194-9.


13. Kakkar A, Tyagi A, Nabi N, Sethi AK, Verma UC. Comparision of clonidine and dexmedetomidine for attenuation of laryngoscopy and intubation response - A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth 2016; 33: 283-8.


14. Scheinin B, Lindgren L, Randell T, Scheinin H, Scheinin M. Dexmedetomidine attenuates sympathoadrenal responses to tracheal intubation and reduces the need for thiopentone and peroperative fentanyl. Br J Anaesth 1992; 68: 126-31.


15. Kumari K, Gombar S, Kapoor D, Sandhu HS. Clinical study to evaluate the role of preoperative dexmedetomidine in attenuation of hemodynamic response to direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan 2015; 53: 123-30.


16. Lu C, Zhang LM, Zhang Y, Ying Y, Li L, Xu L, et al. Intranasal dexmedetomidine as a sedative premedication for patients undergoing suspension laryngoscopy: a randomized double-blind study. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0154192.



17. Niyogi S, Biswas A, Chakraborty I, Chakraborty S, Acharjee A. Attenuation of haemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation with dexmedetomidine: a comparison between intravenous and intranasal route. Indian J Anaesth 2019; 63: 915-23.



18. Dogru K, Arik T, Yildiz K, Bicer C, Madenoglu H, Boyaci A. The effectiveness of intramuscular dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic responses during tracheal intubation and anesthesia induction of hypertensive patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 2007; 68: 292-302.



19. Zanaty OM, El Metainy SA. A comparative evaluation of nebulized dexmedetomidine, nebulized ketamine, and their combination as premedication for outpatient pediatric dental surgery. Anesth Analg 2015; 121: 167-71.


20. Abdel-Ghaffar HS, Kamal SM, El Sherif FA, Mohamed SA. Comparison of nebulised dexmedetomidine, ketamine, or midazolam for premedication in preschool children undergoing bone marrow biopsy. Br J Anaesth 2018; 121: 445-52.


21. Chernik DA, Gillings D, Laine H, Hendler J, Silver JM, Davidson AB, et al. Validity and reliability of the Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale: study with intravenous midazolam. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1990; 10: 244-51.

22. Joffe AM, Deem SA. Physiologic and pathophysiologic responses to intubation. In: Airway Management. 3rd ed. Edited by Benumof J Hagberg CA: Philadelphia, Elsevier Saunders. 2012, pp 184-95.
23. Basar H, Akpinar S, Doganci N, Buyukkocak U, Kaymak C, Sert O, et al. The effects of preanesthetic, single-dose dexmedetomidine on induction, hemodynamic, and cardiovascular parameters. J Clin Anesth 2008; 20: 431-6.


24. Lawrence CJ, De Lange S. Effects of a single pre-operative dexmedetomidine dose on isoflurane requirements and peri-operative haemodynamic stability. Anaesthesia 1997; 53: 736-44.

25. Mahajan L, Kaur M, Gupta R, Aujla KS, Singh A, Kaur A. Attenuation of the pressor responses to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation with intravenous dexmedetomidine versus magnesium sulphate under bispectral index-controlled anaesthesia: a placebo-controlled prospective randomised trial. Indian J Anaesth 2018; 62: 337-43.



26. Yildiz M, Tavlan A, Tuncer S, Reisli R, Yosunkaya A, Otelcioglu S. Effect of dexmedetomidine on haemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation: perioperative haemodynamics and anaesthetic requirements. Drugs R D 2006; 7: 43-52.


27. Kim SH, Oh YJ, Park BW, Sim J, Choi YS. Effects of single-dose dexmedetomidine on the quality of recovery after modified radical mastectomy: a randomised controlled trial. Minerva Anestesiol 2013; 79: 1248-58.

28. Geng ZY, Liu YF, Wang SS, Wang DX. Intra-operative dexmedetomidine reduces early postoperative nausea but not vomiting in adult patients after gynaecological laparoscopic surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2016; 33: 761-6.


29. Christensen AM, Willemoes-Larsen H, Lundby L, Jakobsen KB. Postoperative throat complaints after tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth 1994; 73: 786-7.