|
 |
|
|
Abstract
General anesthetics produce a widespread neurodepression in the central nervous system by enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission and reducing excitatory neurotransmission. However, the action mechanisms of general anesthetics are not completely understood. Moreover, the general anesthetic state comprises multiple components (amnesia, unconsciousness, analgesia, and immobility), each of which is mediated by different receptors and neuronal pathways. Recently, neurotransmitter- and voltage-gated ion channels have emerged as the most likely molecular targets for general anesthetics. The γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors are leading candidates as a primary target of general anesthetics. This review summarizes current knowledge on how anesthetics modify GABAA receptor function.
The introduction of general anesthesia is evaluated as one of the prominent achievements for the development of modern medical science. Since William Morton conducted an operation by using general anesthetics for the first time, the mechanism has not been clearly understood yet.
Still, there is no objectively agreed definition of general anesthesia. The behavioral responses are various depending on the concentration of anesthetics, and can include amnesia, excitation, analgesia, hypnosis and hyperreflexia in a low concentration, and deep sedation, muscle relaxation, and reduced motor and autonomic response to noxious stimuli in a high concentration [1].
Many studies have been recently done on the mechanisms of general anesthesia. Each of the behavioral responses of general anesthesia selectively functions on different parts of the brain and various molecular targets. In particular, the binding sites of ion channel receptors are closely related to the functional sites of general anesthetics. Out of various ion channels, the γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) subunit receptor has been known to play the most important role as a functional site of general anesthetics [1-5]. Therefore, in this review, the physiologic action of the GABAA receptor and the association between various behavioral responses to general anesthetics and the GABAA receptor are summarized from recent pieces of research. In addition, other ion channels that are known to be other functional sites of general anesthetics are also briefly introduced.
The association between the functions of general anesthetics and specific sites of CNS has been recently discovered. The immobility function of inhalation anesthetics by noxious stimuli primarily acts on the spinal cord, not being connected with the brain [6].
Although there is insufficient evidence to prove the association between specific sites of the brain and the functional sites of general anesthetics, there are some cases that are gradually revealed. The amnesia effect of general anesthetics is closely related with the hippocampus [7,8]. Sedation is related to the neocortex [9] and thalamus [10], and hypothalamus is presumably the hypnotic action part.
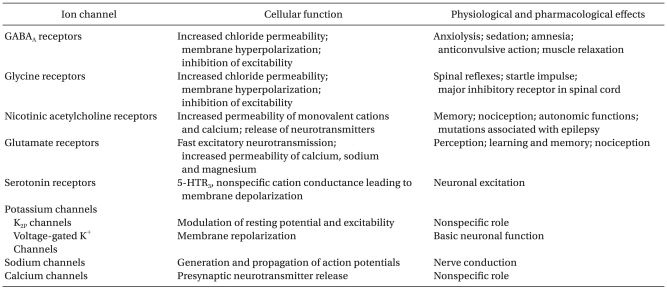
Cells of the brain communicate with each other using a wide variety of chemical neurotransmitters. Such neurotransmitters, responding to electrical signals, are released into synapse. Depending on the functions, they are classified as excitatory neurotransmitters or inhibitory neurotransmitters. Excitatory neurotransmitters, for example glutamate and acetylcholine, cause depolarization. Conversely, inhibitory neurotransmitters, such as α-aminobutyric acid (GAGA) and glycine, reduce postsynaptic activity. The free neurotransmitters bind with ion channel receptors to control the flow of ions. The control of cell electrical activity by ion channels is closely linked with the physiologic action of anesthetics and the various behavioral response patterns to them (Table 1) [11]. Among ion channels, GABAA, glycine, nicotinic acetylcholine, and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors show sensitivity to general anesthetics [1-4]. Some of the volatile anesthetics also act on potassium channels and voltage-gated channels (sodium, calcium) [12-14]. Typically, general anesthetics potentiate the activation of inhibitory postsynaptic channels or inhibit the activation of excitatory synaptic channels [11].
GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain, and as many as one-third of all synapses are GABAergic [15]. Most inhibition is mediated by GABAA receptors, which are chloride-permeable ligand-gated ion channels. Activation of GABAA receptors generally leads to an influx of chloride, hyperpolarization of the cell membrane, shunting of excitatory input, and reduced excitability of the neurons [11]. The GABAA receptor itself is a heteropentameric complex composed of five different subunits, and 19 subunits (α1-6, β1-3, γ1-3, δ, ε, ψ, π and ρ1-3) have been known until now [16]. The combinations of α, β, and γ subunits are the most common with the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. The γ subunit may be replaced by a δ or ε subunit, depending on the brain region. The subunit composition can alter the biophysical properties of the receptors and drug sensitivity [17].
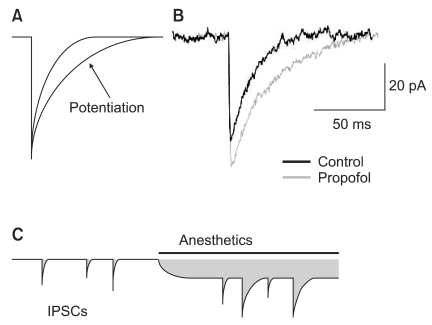
GABAA receptors clustered at postsynaptic terminals are activated by a near-saturating concentration of GABA. GABA transmits information to inhibitory synapse by generating the fast and transient inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) (Fig. 1) [18]. For many years, enhancement of fast synaptic inhibition was widely thought to be the primary mechanism underlying the actions of many GABAergic drugs.
Over the past decade, however, a persistent form of tonic inhibition has been identified in several brain regions. Tonic currents are known to be generated as GABA acts on the GABAA receptor at the extrasynapse, not on synapse (Fig. 1) [8,19]. This tonic inhibitory conductance is generated by high-affinity, slowly desensitizing GABAA receptors that are activated by low ambient concentration of GABA [20-22]. Tonic currents are generated in several types of cells including CA1 pyramidal [8,23], granule cells [24], and interneurons [19,25] of the hippocampus. In the hippocampus, the tonic conductance is also activated by GABA released by action potential dependent vesicular mechanism [26]. The tonic conductance has been shown to regulate neuronal excitability and information processing [19,27].
General anesthetics enhance the action of the neurotransmitter GABA on the GABAA receptor. They potentiate IPSCs generated by the synaptic GABAA receptor [1,2,28]. In addition, several anesthetics have been shown to reduce desensitization of GABAA receptors [28,29] (Fig. 2A and B). At higher concentration, anesthetics directly activate GABAA receptors without the help of GABA [28].
The tonic currents generated by the extrasynaptic GABAA receptors are also potentiated by general anesthetics [7,21,22]. The enhancement of inhibitory currents by general anesthetics is called charge transfer. The increase of charge transfer by tonic currents is 2-3 times larger than that by miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) (Fig. 2C) [23]. Thus, the tonic current function of anesthesia is drawing increasing attention. The difference in pharmacological and kinetic properties by synpatic or extrasynaptic GABAA receptors has been known to be caused by the different composition of the subunits [8]. Hence, a number of studies are performed on the various functions of general anesthetics and their relations with GABAA subunits receptors.
Volatile anesthetics are low-potency compounds that influence a variety of receptors at clinically relevant concentrations [1]. In addition, behavioral testing with volatile anesthetics is difficult for practical reasons. Nonetheless, α1, β1 and β3 subunits of the GABAA receptor have been known as the important functional sites of volatile anesthetics [30,31]. Particularly, two amino acids in the of α1 subunit are critical for anesthetic action: serine 270 in the transmembrane 2 region and alanine 291 near the extracellular regions of transmembrane 3 [30]. Various GABAA subunit receptors have been recognized as being related to the inhibition of the nervous system.
The impairment of memory is one of the most potent effects of many general anesthetics. Memory is particularly sensitive to general anesthetics because amnesia occurs at concentrations well below those that cause sedation and analgesia [32]. The dose of etomidate that impairs memory is considerably lower than the dose that causes immobility [7]. In the case of isoflurane, reduced cognitive function and amnesia are caused at a concentration remarkably lower than 1 MAC [8]. GABAergic tonic currents occurring in the hippocampus are closely connected with memory, playing an important role in cognition [7,8]. Low concentration of propofol [33], etomidate [7], and isoflurane [8] enhance the tonic currents through the α5 GABAA receptors in the hippocampus. Although the ratio of the GABAA receptor subunits that have α5 is low, they are distributed at the extrasynapse of the hippocampus in a relatively high ratio [34,35]. Some researches show that α5GABAA subunit receptors are related to learning and memory. The mice with chromosomal depletion (α5-/-) at the α5GABAA subunit receptor showed better hippocampus-dependent learning than those of the wild type [36]. The memory of mice was improved when the position 105 histidine of α5 subunit was substituted with arginine (α5His105Arg) [37]. Therefore, it can be assumed that general anesthetics potentiate the tonic currents acting on the α5GABAA receptor in the hippocampus, which can be considered as one of the amnesia mechanisms that occur during anesthesia.
Sedation refers to a decreased level of arousal, as indicated by longer response times, decreased motor activity, and slurred speech. In animal models, sedation is assessed by the levels of reduced motor activity and arousal [38]. Sedation by etomidate occurs at another isoform of the α5GABAA receptor related to amnesia. In β2 subunit (β2Asn265Ser) mice, low doses of etomidate failed to reduce spontaneous locomotor activity, which implies that the sedative actions of etomidate depend on GABAA receptors containing the β2 subunit [39]. Diazepam, which has distinct sedation activity, is related to the position 101 histidine of the α1 subunit [40]. The α1 and β2 subunit-containing GABAA receptors in the neocortex are thought to contribute to the sedative actions of several inhaled anesthetics [9]. Tonic current in the thalamic VB neurons may contribute to the sedative action [10].
Hypnosis typically requires higher concentrations of anesthetics than sedation and is often measured by the loss of the righting reflex in rodents [38]. Etomidate induced hypnosis also depends on the β3 (Asn256Met) subunit, being partly related with the GABAA receptor β2 subunit, as well [41]. Hypnosis by anesthetics is presumed to be related with the thalamus [42] and the tuberomammillary nucleus of the hypothalamus [43], though it is yet unproved.
The glycine receptor is known as an important target of inhalation anesthetics in the spinal cord [6]. This receptor, composed of four α subunits and a single β subunit, shows the inhibitory function by enhancing the inflow of chloride ions into the cells, the same as GABAA receptors. It has been known that the glycine receptor is particularly strong for the loss of response to a painful stimulus, which appears to be determined predominantly by actions in the spinal cord [6,44].
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are also involved in the control of synaptic conduction in CNS. Activation of this receptor causes excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) by the inflow of cation into the cells. It has been known that general anesthetics show the repressive function by blocking EPSCs at a low concentration [45].
The voltage-gated sodium channel plays an important role in axonal conduction, synaptic integration, and neuronal excitation [5]. General anesthetics, particularly, inhibit the presynaptic voltage-gated sodium channels in glutamatergic synapse, which inhibits the excitation of the neuron by blocking the release of presynaptic neurotransmitters [5,13].
It has been conventionally known that general anesthetics act on CNS non-specifically. However, there has recently been much progress in understanding the functional mechanisms, as well. Most of the general anesthetics act on various neurotransmitter-gated ion channels. The most known representative target is the GABAA receptor. Especially thanks to the advancement in genetic engineering, the ways in which various behavioral response patterns are selectively related to the GABAA receptor subunits in specific parts of the brain have been gradually revealed. Such progress not only increases the understanding of the mechanisms of general anesthetics, but also provides help in developing novel and selective anesthetics.
References
1. Campagna JA, Miller KW, Forman SA. Mechanisms of actions of inhaled anesthetics. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 2110-2124. PMID: 12761368.


2. Hemmings HC Jr, Akabas MH, Goldstein PA, Trudell JR, Orser BA, Harrison NL. Emerging molecular mechanisms of general anesthetic action. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2005; 26: 503-510. PMID: 16126282.


3. Orser BA, Canning KJ, Macdonald JF. Mechanisms of general anesthesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2002; 15: 427-433. PMID: 17019234.


4. Franks NP. Molecular targets underlying general anaesthesia. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 147(Suppl 1): S72-S81. PMID: 16402123.



5. Hemmings HC Jr. Sodium channels and the synaptic mechanisms of inhaled anaesthetics. Br J Anaesth 2009; 103: 61-69. PMID: 19508978.



6. Sonner JM, Antognini JF, Dutton RC, Flood P, Gray AT, Harris RA, et al. Inhaled anesthetics and immobility: mechanisms, mysteries, and minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration. Anesth Analg 2003; 97: 718-740. PMID: 12933393.


7. Cheng VY, Martin LJ, Elliott EM, Kim JH, Mount HT, Taverna FA, et al. Alpha5GABAA receptors mediate the amnestic but not sedative-hypnotic effects of the general anesthetic etomidate. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 3713-3720. PMID: 16597725.



8. Caraiscos VB, Newell JG, You-Ten KE, Elliott EM, Rosahl TW, Wafford KA, et al. Selective enhancement of tonic GABAergic inhibition in murine hippocampal neurons by low concentrations of the volatile anesthetic isoflurane. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 8454-8458. PMID: 15456818.



9. McKernan RM, Whiting PJ. Which GABAA-receptor subtypes really occur in the brain? Trends Neurosci 1996; 19: 139-143. PMID: 8658597.


10. Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Frolund B, Liljefors T, Ebert B. GABA(A) agonists and partial agonists: THIP (Gaboxadol) as a non-opioid analgesic and a novel type of hypnotic. Biochem Pharmacol 2004; 68: 1573-1580. PMID: 15451401.


11. Pearce RA. Edited by Antognini JF, Carstens EE, Raines DEGeneral anesthetic effects on GABAA receptors. Neural Mechanisms of Anesthesia. 2003, : New Jersey, Humana Press. pp 265-282.
12. Franks NP, Honore E. The TREK K2P channels and their role in general anaesthesia and neuroprotection. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004; 25: 601-608. PMID: 15491783.


13. Ouyang W, Wang G, Hemmings HC Jr. Isoflurane and propofol inhibit voltage-gated sodium channels in isolated rat neurohypophysial nerve terminals. Mol Pharmacol 2003; 64: 373-381. PMID: 12869642.


14. Kamatchi GL, Chan CK, Snutch T, Durieux ME, Lynch C 3rd. Volatile anesthetic inhibition of neuronal Ca channel currents expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Brain Res 1999; 831: 85-96. PMID: 10411986.


15. Bloom FE, Iversen LL. Localizing 3H-GABA in nerve terminals of rat cerebral cortex by electron microscopic autoradiography. Nature 1971; 229: 628-630. PMID: 4925465.


16. Macdonald RL, Olsen RW. GABAA receptor channels. Annu Rev Neurosci 1994; 17: 569-602. PMID: 7516126.


17. Barnard EA, Skolnick P, Olsen RW, Mohler H, Sieghart W, Biggio G, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev 1998; 50: 291-313. PMID: 9647870.

18. Maconochie DJ, Zempel JM, Steinbach JH. How quickly can GABAA receptors open? Neuron 1994; 12: 61-71. PMID: 8292360.


19. Semyanov A, Walker MC, Kullmann DM, Silver RA. Tonically active GABAA receptors: modulating gain and maintaining the tone. Trends Neurosci 2004; 27: 262-269. PMID: 15111008.


20. Brickley SG, Cull-Candy SG, Farrant M. Development of a tonic form of synaptic inhibition in rat cerebellar granule cells resulting from persistent activation of GABAA receptors. J Physiol 1996; 497: 753-759. PMID: 9003560.



21. Yeung JY, Canning KJ, Zhu G, Pennefather P, Macdonald JF, Orser BA. Tonically activated GABAA receptors in hippocampal neurons are high-affinity, low-conductance sensors for extracellular GABA. Mol Pharmacol 2003; 63: 2-8. PMID: 12488530.


22. Bai D, Pennefather PS, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. The general anesthetic propofol slows deactivation and desensitization of GABA(A) receptors. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 10635-10646. PMID: 10594047.



23. Bai D, Zhu G, Pennefather P, Jackson MF, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of tonic and quantal inhibitory postsynaptic currents mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors in hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol 2001; 59: 814-824. PMID: 11259626.


24. Nusser Z, Mody I. Selective modulation of tonic and phasic inhibitions in dentate gyrus granule cells. J Neurophysiol 2002; 87: 2624-2628. PMID: 11976398.


25. Stell BM, Mody I. Receptors with different affinities mediate phasic and tonic GABA(A) conductances in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 2002; 22: RC223PMID: 12006605.



26. Glykys J, Mody I. The main source of ambient GABA responsible for tonic inhibition in the mouse hippocampus. J Physiol 2007; 582: 1163-1178. PMID: 17525114.



27. Bonin RP, Martin LJ, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. Alpha5GABAA receptors regulate the intrinsic excitability of mouse hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 2007; 98: 2244-2254. PMID: 17715197.


28. Orser BA, McAdam LC, Roder S, MacDonald JF. General anaesthetics and their effects on GABA(A) receptor desensitization. Toxicol Lett 1998; 100-101: 217-224. PMID: 10049145.


29. Orser BA, Wang LY, Pennefather PS, MacDonald JF. Propofol modulates activation and desensitization of GABAA receptors in cultured murine hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 1994; 14: 7747-7760. PMID: 7996209.



30. Mihic SJ, Ye Q, Wick MJ, Koltchine VV, Krasowski MD, Finn SE, et al. Sites of alcohol and volatile anaesthetic action on GABA(A) and glycine receptors. Nature 1997; 389: 385-389. PMID: 9311780.


31. Siegwart R, Jurd R, Rudolph U. Molecular determinants for the action of general anesthetics at recombinant alpha(2)beta(3) gamma(2)gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors. J Neurochem 2002; 80: 140-148. PMID: 11796752.


32. Pain L, Angst MJ, LeGourrier L, Oberling P. Effect of a nonsedative dose of propofol on memory for aversively loaded information in rats. Anesthesiology 2002; 97: 447-453. PMID: 12151936.


33. Bieda MC, MacIver MB. Major role for tonic GABAA conductances in anesthetic suppression of intrinsic neuronal excitability. J Neurophysiol 2004; 92: 1658-1667. PMID: 15140905.


34. Wainwright A, Sirinathsinghji DJ, Oliver KR. Expression of GABA(A) receptor alpha5 subunit-like immunoreactivity in human hippocampus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2000; 80: 228-232. PMID: 11038255.


35. Sur C, Fresu L, Howell O, McKernan RM, Atack JR. Autoradiographic localization of alpha5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 1999; 822: 265-270. PMID: 10082908.


36. Collinson N, Kuenzi FM, Jarolimek W, Maubach KA, Cothliff R, Sur C, et al. Enhanced learning and memory and altered GABAergic synaptic transmission in mice lacking the alpha 5 subunit of the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 5572-5580. PMID: 12097508.



37. Crestani F, Keist R, Fritschy JM, Benke D, Vogt K, Prut L, et al. Trace fear conditioning involves hippocampal alpha5 GABA(A) receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002; 99: 8980-8985. PMID: 12084936.



38. Rudolph U, Antkowiak B. Molecular and neuronal substrates for general anaesthetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 2004; 5: 709-720. PMID: 15322529.


39. Reynolds DS, Rosahl TW, Cirone J, O'Meara GF, Haythornthwaite A, Newman RJ, et al. Sedation and anesthesia mediated by distinct GABA(A) receptor isoforms. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 8608-8617. PMID: 13679430.



40. Rudolph U, Crestani F, Benke D, Brünig I, Benson JA, Fritschy JM, et al. Benzodiazepine actions mediated by specific gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptor subtypes. Nature 1999; 401: 796-800. PMID: 10548105.


41. Jurd R, Arras M, Lambert S, Drexler B, Siegwart R, Crestani F, et al. General anesthetic actions in vivo strongly attenuated by a point mutation in the GABA(A) receptor beta3 subunit. FASEB J 2003; 17: 250-252. PMID: 12475885.


42. Belelli D, Peden DR, Rosahl TW, Wafford KA, Lambert JJ. Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors of thalamocortical neurons: a molecular target for hypnotics. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 11513-11520. PMID: 16354909.



43. Nelson LE, Guo TZ, Lu J, Saper CB, Franks NP, Maze M. The sedative component of anesthesia is mediated by GABA(A) receptors in an endogenous sleep pathway. Nat Neurosci 2002; 5: 979-984. PMID: 12195434.


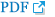
44. Ouyang W, Hemmings HC Jr. Depression by isoflurane of the action potential and underlying voltage-gated ion currents in isolated rat neurohypophysial nerve terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005; 312: 801-808. PMID: 15375177.


45. Flood P, Ramirez-Latorre J, Role L. Alpha 4 beta 2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system are inhibited by isoflurane and propofol, but alpha 7-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are unaffected. Anesthesiology 1997; 86: 859-865. PMID: 9105230.


46. Lin LH, Chen LL, Harris RA. Enflurane inhibits NMDA, AMPA, and kainate-induced currents in Xenopus oocytes expressing mouse and human brain mRNA. FASEB J 1993; 7: 479-485. PMID: 7681790.


47. Maclver MB, Mikulec AA, Amagasu SM, Monroe FA. Volatile anesthetics depress glutamate transmission via presynaptic actions. Anesthesiology 1996; 85: 823-834. PMID: 8873553.


48. Patel AJ, Honoré E, Lesage F, Fink M, Romey G, Lazdunski M. Inhalational anesthetics activate two-pore-domain background K+ channels. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: 422-426. PMID: 10321245.


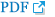
Fig. 1
Synaptic and extrasynaptic activation of γ-aminobutyric acid subtype A (GABAA) receptors. Action potential dependent release of GABA into the synaptic cleft transiently activates GABAA receptors in the postsynaptic membrane. This generates inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs). Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors are activated by low concentrations of GABA in the extracellular space. These receptors have low desensitization rates and can produce a tonic current (continuous current). The tonic current is revealed by application of a GABAA antagonist, Bicuculline, which inhibits the current. Many general anesthetics enhance the tonic current at clinically relevant concentrations. ITonic represents the amplitude of the steady state current.

Fig. 2
Potentiation of γ-aminobutyric acid subtype A (GABAA) receptor-mediated inhibitory synaptic and tonic current by the general anesthetics. (A) The prolongation of miniature inhibitory synaptic currents (mIPSCs) by the slowing of current decay is shown. (B) Propofol prolongs the time-course of mIPSCs and slightly increases the peak amplitude of mIPSCs. (C) The schematic drawings used to calculate charge transfer (shaded area). Anesthetics produce a greater increased in charge transfer associated with the tonic current compared with mIPSCs.
- TOOLS