|
 |
| Korean J Anesthesiol > Volume 75(3); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Methods
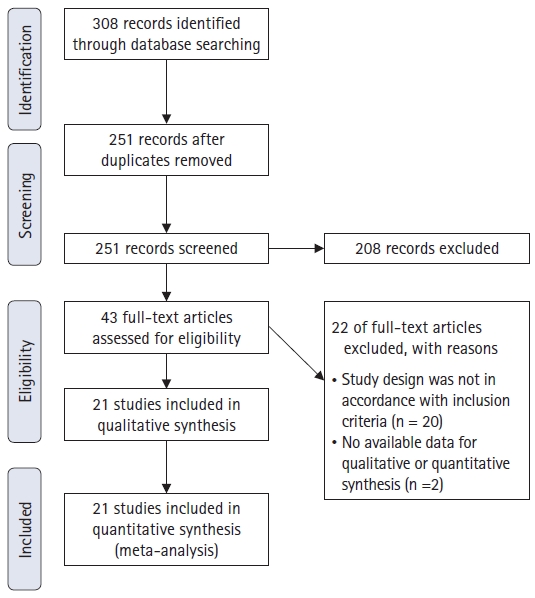
Results
NOTES
Funding
This work was supported by research funding from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2019R1G1A1099660).
Author Contributions
Yumin Jo (Writing – original draft; Writing – review & editing)
Seyeon Park (Data curation; Formal analysis; Methodology; Visualization)
Chahyun Oh (Investigation; Software; Validation)
Yujin Pak (Methodology; Project administration; Resources)
Kuhee Jeong (Visualization; Writing – review & editing)
Sangwon Yun (Visualization; Writing – review & editing)
Chan Noh (Formal analysis; Resources; Validation)
Woosuk Chung (Conceptualization; Writing – review & editing)
Yoon-Hee Kim (Resources; Supervision; Writing – review & editing)
Young Kwon Ko (Conceptualization; Supervision; Writing – review & editing)
Boohwi Hong (Conceptualization; Data curation; Supervision; Writing – original draft; Writing – review & editing)
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Material 2.
Supplementary Material 3.
Supplementary Material 4.
Supplementary Material 6.
Fig. 2.
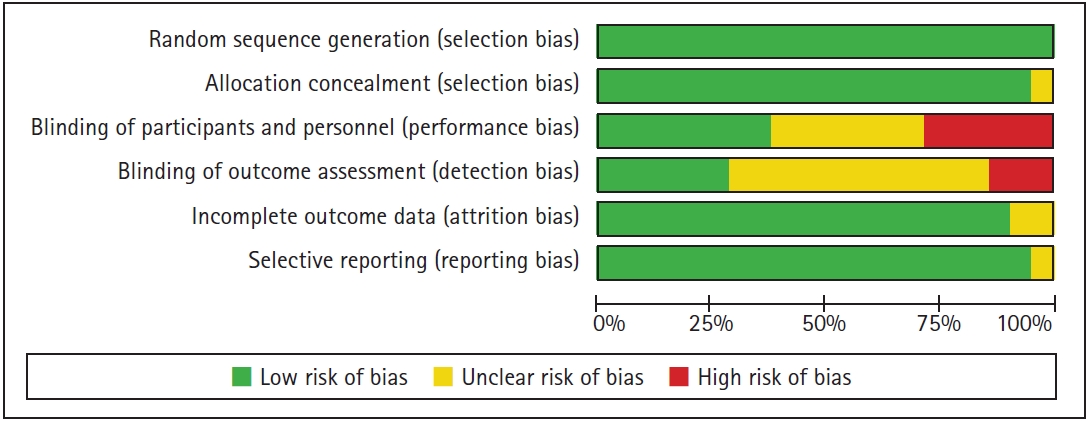
Fig. 3.
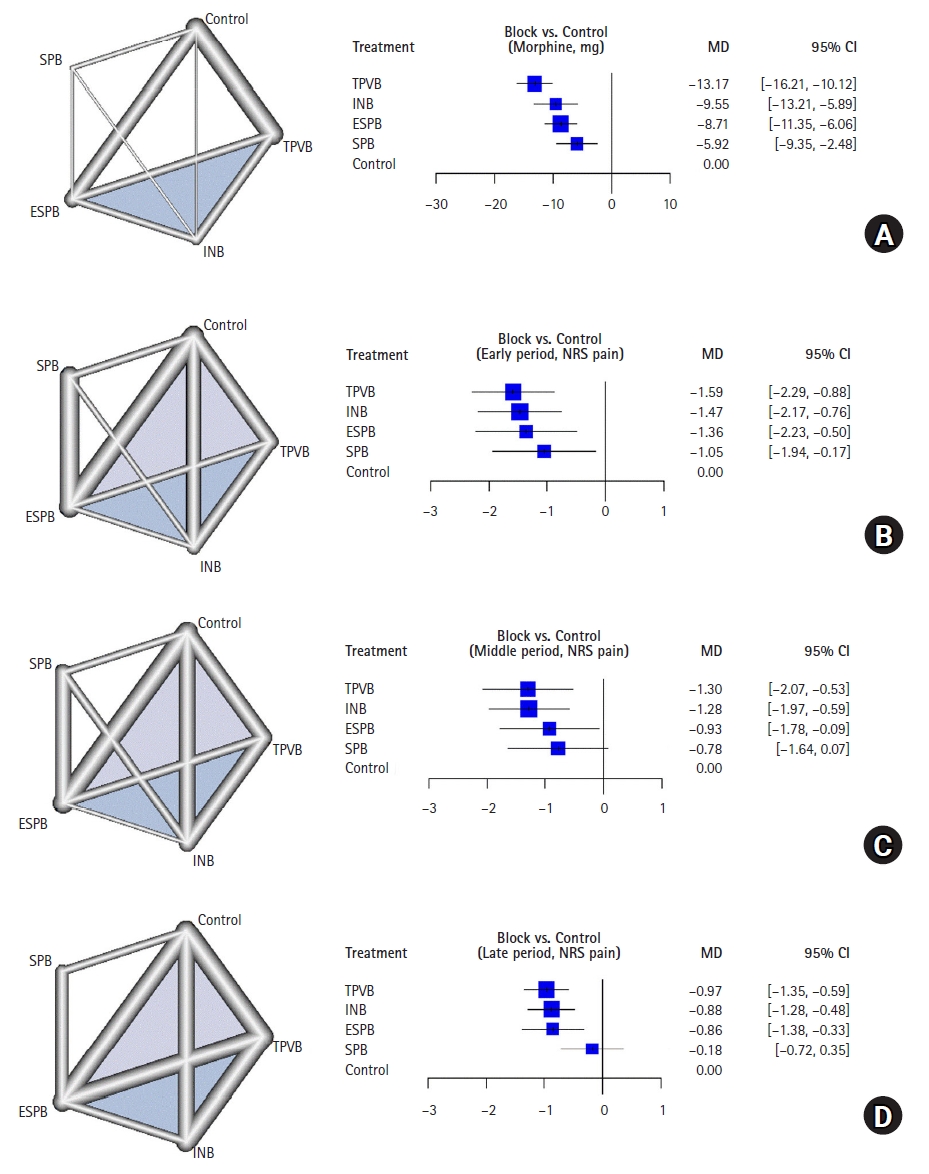
Table 1.
| Author & Year | Country | Surgery | Port | Group(s) (n) | Block level | Localization | Local anesthetics | Block timing | Opioid data | Pain score data representation method (early, middle, late period [h]) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu, 2021 [25] | China | Lobectomy, wedge resection, segmentectomy | 1 | ESPB (40); control (40) | T5 | Ultrasound | 25 ml of 0.4% ropivacaine | Before induction | Sufentanil | Table (2, 8, 24) |
| Hu, 2021 [26] | China | Wedge resection | 1 | TPVB (30); control (30) | T4, intrathoracic approach | Thoracoscopic-assisted | 20 ml of 0.375% ropivacaine | End of surgery | Sufentanil | Table (6, 12, 24) |
| Zhao, 2020 [27] | China | Lobectomy, wedge resection, segmentectomy | NA | ESPB (33); TPVB (33) | ESPB: T4 and T6 | Ultrasound | 30 ml of 0.4% ropivacaine | Before induction | Oxycodone | Table (NA, NA, 24) |
| Yao, 2020 [28] | China | Lobectomy, segmentectomy | NA | ESPB (37); control (38) | T5 | Ultrasound | 25 ml of 0.5% ropivacaine | Before induction | Sufentanil | Table (1, 8, 24) |
| Viti, 2020 [29] | Italy | Lobectomy, segmentectomy | 3 | SPB (46); control (44) | Fifth rib | Ultrasound | 30 ml of 0.3% ropivacaine | After induction | No data | Plot (NA, 6 a.m. to 2 p.m. POD 1, 2 p.m. to 10 p.m. POD 1) |
| Turhan, 2020 [30] | Turkey | Lobectomy, segmentectomy | 2 | ESPB (35); TPVB (35); INB (36) | ESPB, TPVB: fifth rib | ESPB, TPVB: ultrasound | 20 ml of 0.5% ropivacaine | TPVB, ESPB: before induction | Morphine mg equivalent | Table (1, 12, 24) |
| INB: T4–T7 | INB: thoracoscopic-assisted | INB: after induction | ||||||||
| Lee, 2020 [31] | Korea | Lobectomy | 3 | INB (23); SPB (23) | Fifth rib | INB: thoracoscopic-assisted | 20 ml of 0.375% ropivacaine | INB: end of the surgery | Fentanyl | Table (2, 12, 24) |
| SPB: ultrasound | SPB: after induction | |||||||||
| Kim, 2020 [32] | Korea | Wedge resection for primary spontaneous pneumothorax | 1 | INB (25); SPB (25) | Fifth rib | INB: thoracoscopic-assisted | 20 mL of | INB: end of the surgery | Fentanyl, | Table (3, 12, NA) |
| SPB: ultrasound | 0.375% ropivacaine | SPB: after induction | no standard time (chest tube removal) | |||||||
| Finnerty, 2020 [33] | Ireland | Wedge resection, pleurodesis, pleurectomy, lobectomy, decortication, bullectomy, or pleural biopsy | NA | ESPB (30); SPB (30) | T5, fifth rib | Ultrasound | 30 ml of 0.25% levobupivacaine | After induction | Oxycodone | Plot (1, 12, 24) |
| Ciftci, 2020 [34] | Turkey | Lobectomy, wedge resection | 3 | ESPB (30); TPVB (30); control (30) | T5 | Ultrasound | 20 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine | Before induction | Fentanyl, 48 h of data only | Plot (1, 8, 24) |
| Ciftci, 2020 [35] | Turkey | Lobectomy | NA | ESPB (30); control (30) | T5 | Ultrasound | 20 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine | Before induction | Fentanyl | Table (2, 8, 24) |
| Chu, 2020 [36] | China | Lobectomy, wedge resection, segmentectomy | NA | TPVB (25); control (24) | T4, T7 | Ultrasound | 20 ml of 0.375% ropivacaine | Unknown | Sufentanil, no data | Table (1, NA, 24) |
| Cheng, 2020 [37] | China | Lobectomy | 1 | SPB (25) (modified intercostal nerve block); control (25) | Fourth and fifth rib | Ultrasound | 10 ml of 0.35% ropivacaine | After induction | Sufentanil | NA |
| Chen, 2020 [38] | China | Lobectomy, wedge resection, segmentectomy | 2 | TPVB (24); INB (24); ESPB (24) | TPVB: T5, T6, T7 | Ultrasound | 20 ml of 0.375% ropivacaine | After induction | Morphine mg equivalent | Plot (2, 8, 24) |
| INB: T4–T9 | ||||||||||
| ESPB: T5 | ||||||||||
| Gaballah, 2019 [39] | Egypt | Wedge resection, decortication, bullectomy, pleural biopsy, pleurodesis, repair of bronchopleural fistula, diaphragmatic plication | NA | ESPB (30); SPB (30) | ESP: T5 | Ultrasound | 20 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine | After induction | Pethidine | Plot (1, 12, 24) |
| SPB: T7 | ||||||||||
| Wu, 2018 [40] | China | Wedge resection, lobectomy, bilobectomy, pneumonectomy | NA | TPVB (34); INB (32) | TPVB: T5 | Ultrasound | 0.3 ml/kg of 0.5% ropivacaine | Before induction | Sufentanil | Plot (1, 10, 24) |
| INB: fourth and seventh intercostal space | ||||||||||
| Okmen, 2018 [41] | Turkey | Wedge resection, lobectomy | NA | SPB (20); control (20) | Fifth rib | Ultrasound | 20 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine | End of surgery | Tramadol | Table (2, 12, 24) |
| Kim, 2018 [42] | Korea | Lobectomy, wedge resection, segmentectomy | 2 or 3 | SPB (42); control (43) | Fifth rib | Ultrasound | 0.4 ml/kg of 0.375% ropivacaine | After induction | Morphine mg equivalent | Plot (NA, 12, 24) |
| Ahmed, 2017 [43] | Pakistan | Elective diagnostic VATS | NA | INB (30); control (30) | 5 level | Bone landmark | 20 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine | End of surgery | Morphine | Plot (1, 12, 24) |
| Kaya, 2006 [44] | Turkey | Wedge resection, lung biopsy, pleural biopsy | NA | TPVB (25); control (22) | T4–T8, 5 level | Bone landmark | 20 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine | Before induction | Morphine | Table (1, 8, 24) |
| Vogt, 2005 [45] | Switzerland | Biopsy, lung resection, pleurodeses, resection of intrathoracic tumor | NA | TPVB; control | T6 | Bone landmark | 0.4 ml/kg of 0.375% bupivacaine | After induction | Morphine | Plot (1, NA, 24) |
Table 2.
I2: Higgins’ I2, global inconsistency based on the full design-by-treatment interaction random-effects model [21], local inconsistency based on the difference between direct and indirect estimates using the net splitting technique. ESPB: erector spinae plane block, INB: intercostal nerve block, SPB: serratus plane block, TPVB: thoracic paravertebral block, GRADE: grading of recommendations, assessment, development and evaluations.
Table 3.
Estimates are presented as mean differences (95% CI). Mean differences < 0 favor the column intervention and mean differences > 0 favor the row intervention. The upper triangle displays only the pooled effect sizes of the direct comparisons that were available in our network. No direct comparison is expressed in the empty field. The lower triangle contains the estimated effect sizes for each comparison, even those for which only indirect evidence was available. ESPB: erector spinae plane block, INB: intercostal nerve block, SPB: serratus plane block, TPVB: thoracic paravertebral block.